* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chicken Pox
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Anti-nuclear antibody wikipedia , lookup
Globalization and disease wikipedia , lookup
Transmission (medicine) wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Hospital-acquired infection wikipedia , lookup
Innate immune system wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
Hygiene hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Monoclonal antibody wikipedia , lookup
Orthohantavirus wikipedia , lookup
Human cytomegalovirus wikipedia , lookup
Ebola virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Common cold wikipedia , lookup
Marburg virus disease wikipedia , lookup
West Nile fever wikipedia , lookup
Childhood immunizations in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Immunosuppressive drug wikipedia , lookup
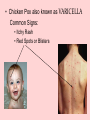
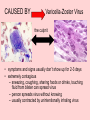
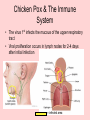
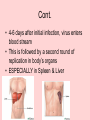
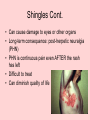
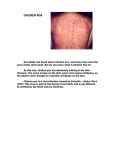
Chicken Pox Dana Willard • Chicken Pox also known as VARICELLA Common Signs: • Itchy Rash • Red Spots or Blisters CAUSED BY Varicella-Zoster Virus the culprit • symptoms and signs usually don’t show up for 2-3 days • extremely contagious – sneezing, coughing, sharing foods or drinks, touching fluid from blister can spread virus – person spreads virus without knowing – usually contracted by unintentionally inhaling virus Early Symptoms • • • • • • Fever Headache Sore Throat Loss of Appetite Fatigue Rash Appears After 2-3 Days Chicken Pox & The Immune System • The virus 1st infects the mucous of the upper respiratory tract • Viral proliferation occurs in lymph nodes for 2-4 days after initial infection = infected area Cont. • 4-6 days after initial infection, virus enters blood stream • This is followed by a second round of replication in body’s organs • ESPECIALLY in Spleen & Liver 1st Exposure • Body 1st Exposed creates antibodies – Immunoglobulin G (IgG) – Immunoglobulin M (IgM) – Immunoglobulin A (IgA) 1st Exposure Cont. • B & T memory cells are also created – If the virus is in the body again, the memory cells will detect it • This will help a faster response • IF there is a 2nd exposure, memory cells will stimulate cells to create antibodies Children • Usually get it around the age of 12 – Can occur earlier or later • Kids get chicken pox easily – They spread germs effectively • It’s not a bad thing for them to get – They’ll create antibodies which will prevent any later infections from occurring Adults • Chickenpox complications are more likely in adults than kids – The blisters/red spots scar easier – Lead to more serious diseases i.e. pneumonia, bone infections, etc. Can Also Cause……. Shingles! • Also caused by Varicella-Zoster Virus – Blistering, painful rashes – Tends to occur on one side of the body • Like torso or face Shingles Cont. • Can cause damage to eyes or other organs • Long-term consequence: post-herpetic neuralgia (PHN) • PHN is continuous pain even AFTER the rash has left • Difficult to treat • Can diminish quality of life • Expose kids at a young age • They will make antibodies to prevent any second exposures to the virus • Easier to treat • Prevent Shingles and other complications