* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Earth History - 8th Grade Science
Chagas disease wikipedia , lookup
Herpes simplex virus wikipedia , lookup
Influenza A virus wikipedia , lookup
Orthohantavirus wikipedia , lookup
Brucellosis wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
Meningococcal disease wikipedia , lookup
Typhoid fever wikipedia , lookup
Sexually transmitted infection wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Middle East respiratory syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Henipavirus wikipedia , lookup
Rocky Mountain spotted fever wikipedia , lookup
Neglected tropical diseases wikipedia , lookup
Onchocerciasis wikipedia , lookup
Eradication of infectious diseases wikipedia , lookup
Ebola virus disease wikipedia , lookup
West Nile fever wikipedia , lookup
Visceral leishmaniasis wikipedia , lookup
Leishmaniasis wikipedia , lookup
African trypanosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Marburg virus disease wikipedia , lookup
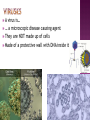
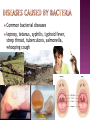
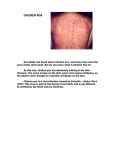
microbiology - the study of microbes Microbes – organisms that can only be seen under a microscope ...this is what happens when you leave beef (L) or chicken (R) on the counter: it grows E. coli, Salmonella, and Shigella! A virus is… … a microscopic disease causing agent They are NOT made up of cells Made of a protective wall with DNA inside it made of cells containing DNA respond to stimuli take in energy and export waste reproduce grow ( self propelled movement) Are they alive? Yes Reproduce No Don’t eat or produce waste, are not made of cells, need a host (virus video) Childhood diseases… Chicken Pox, small pox, yellow fever, warts Other diseases … Colds, Influenza (the flu), meningitis, west nile, ebola What does NOT work on viruses? Vaccines are used to treat viruses What type of vaccines do you know of? Bacteria are… … prokaryotic organisms ( the smallest living thing) Where do they live? Soil, Radioactive waste, Water, Plants, Humans, Deep in the earth's crust, Arctic ice, Glaciers, Hot springs, The stratosphere (between 6 to 30 miles up in the atmosphere), Ocean depths How do we classify bacteria? By 3 different shapes Spherical Usually the simplest ones. These bacteria are called cocci (singular coccus). Rod shaped These are known as bacilli (singular bacillus). Spiral These are known as spirilla (singular spirillus). Common bacterial diseases leprosy, tetanus, syphilis, typhoid fever, strep throat, tuberculosis, salmonella, whooping cough What is a vector? Animal disease spreaders that don’t catch the illness They carry infectious disease (can be passed from one generation to the next) Examples… Rats, ticks, and mosquitoes What do scientists study? Microbial pathogens – disease causing agents Examples? Virus, Bacteria, Parasite How do they study pathogens? Computer modeling, cell cultures, animals, clinical trials STARTED COMPLETED NOT COMPLETED Serious Adverse Event Adverse Event Protocol Violation Lost to Follow-up Withdrawal by Subject Fluzone® High Dose 6108 5697 411 36 0 60 208 107 Fluzone® 3050 2835 215 17 2 27 103 66 How are diseases spread? What happens when they spread rapidly? Epidemic a disease that is wide spread in a particular area Pandemic An epidemic that spreads over a wide area An epidemic may be localized to a small region but the number of people affected may be very, very large compared to what is "expected". In this case, it can be called a pandemic even if its geographical spread is not very large. For example, let us say that a disease has an "expected" rate of infection of 15%. When 40% of the population of a state is infected, we have an epidemic on our hands. When 75% of the population is infected, it has reached pandemic proportions. 1. The name of the disease I am studying is chicken pox. It gets its name from the way it looks like the bumps on a chicken’s skin. 2. A virus causes chicken pox. 3. The symptoms of this disease are first a fever, headache, stomach ache, and then small itchy spots appear on your skin. 4. It is transmitted through the air or by physical contact. 5. You are not likely to catch it because most people get vaccinated for it, or have already had it.