* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download FBA-BIP
Conservation psychology wikipedia , lookup
Insufficient justification wikipedia , lookup
Social Bonding and Nurture Kinship wikipedia , lookup
Attitude change wikipedia , lookup
Social psychology wikipedia , lookup
Bullying and emotional intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Prosocial behavior wikipedia , lookup
Parent management training wikipedia , lookup
Behavioral modernity wikipedia , lookup
Counterproductive work behavior wikipedia , lookup
Psychological behaviorism wikipedia , lookup
Abnormal psychology wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Observational methods in psychology wikipedia , lookup
Organizational behavior wikipedia , lookup
Symbolic behavior wikipedia , lookup
Social perception wikipedia , lookup
Verbal Behavior wikipedia , lookup
Impression formation wikipedia , lookup
Applied behavior analysis wikipedia , lookup
Thin-slicing wikipedia , lookup
Operant conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Attribution (psychology) wikipedia , lookup
Theory of planned behavior wikipedia , lookup
Transtheoretical model wikipedia , lookup
Behavior analysis of child development wikipedia , lookup
Theory of reasoned action wikipedia , lookup
Behaviorism wikipedia , lookup
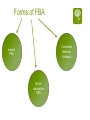
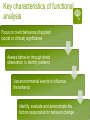
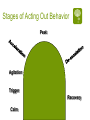
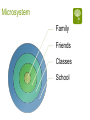
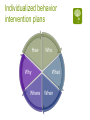
Functional Behavior Analysis Orv C. Karan, Ph.D. Professor of Education University of Connecticut Introduction Behavior Problems: Fitting square pegs into round holes What is a Behavior Problem? Relative to the accepted codes of conduct of the situation/setting/culture the person’s behavior: Can be excessive Can be deficient Often a combination of too much of one type of behavior and not enough of another Can be crisis Behavior Problems Like truth, beauty and a contact lens are often in the eye of the beholder Often called interfering or target behaviors Require interventions that: (1) minimize or eliminate problem behaviors, and (2) result in socially acceptable behaviors One’s behavior is determined to be acceptable/problematic relative to: Laws Rules and policies Moral, ethical and professional codes of conduct Cultural, ethnic and religious practices Peer and reference groups Competency-deviancy hypothesis The more competent a person is perceived to be the more deviant society allows them to be -Celebrities, famous athletes, people of wealth, etc. The less competent a person is perceived to be the less deviant society allows them to be -People who are poor, disabled, homeless, institutionalized, etc. School behavior management approaches Rules and policies School awards Detention Principal’s office Suspension Expulsion Classroom behavior management approaches Public acknowledgement vs. public humiliation (mild) Level or point system with access to privileges Group dependent, group inter-dependent and group independent practices Teacher Assessments Start on the first day of class Called “sizing up” and its done by instinct and intuition Have effects that are quite stable Can have profound effects on students’ perceptions of themselves and their interactions with their teachers Some student characteristics that influence teachers’ perceptions of their abilities Eye contact Facial expressions Way they dress Body posture Way they sit in class Way they talk in class Cooperativeness All behavior is communication Applies to all individuals in human interactions Cannot not communicate 65% or more of all communication is non-verbal Examples of perceptions of other’s intent “He knows what’s he’s supposed to do but chooses not to do it” “He’s just being manipulative” “She’s testing me” “She’s lazy” “She’s disrespecting me” “He understands everything” Road rage How well do you perceive the truth? FINISHED FILES ARE THE RESULT OF YEARS OF SCIENTIFIC STUDY COMBINED WITH EXPERIENCE OF MANY YEARS Communication cautions Communication styles differ from person to person Others may not mean what we believe they do Many times different ways of talking or behaving are causing a problem Layers of communication are always at work in communication Anything one says or does can send messages that become part of the meaning we impart to our interactions Communication/ Miscommunication (Complimentary Schismogenesis) Emotions / Feelings Interpretations Perceptions Interpretations Action / Behavior Feelings / Emotions Perceptions Sensations Action / Behavior Sensations B = f (p,e) Behavior is a function of the person in his/her environment Environmental variables are better predictors of behavior than are individual characteristics or traits Function v. Form Function of behavior is more important than its form What is the student communicating with his/her behavior? How is that student’s behavior being interpreted by others? How are others reacting to the student? What happens to the student’s behavior? Communicative Functions of Behavior Self-regulation Reflecting an emotional or physical state Responding to something Wanting to influence the environment Having fun Skill limitation Rationale for using Functional Behavior Analysis (FBA) Mandated by IDEA To try identifying the function of behavior Best practice Genesis of FBA Thorndike’s Law of effect, i.e., building S-R connections through trial an error Watson’s work led to idea that the presentation of some stimuli will cause behavior to occur (respondent behavior) Pavlov Genesis of FBA continued… Skinner’s work showed that behavior was driven by consequences that follow it (operant behavior) Bijou’s work led to A-B-C approach which is the foundation of FBA Legal Aspects of FBA In response to disciplinary action for a child with special needs the IEP team must meet within 10 days to develop an FBA plan to either develop, review or revise an existing BIP Key elements of FBA Behavior is operationally defined Behavior can be predicted to occur Function of behavior is defined A behavior intervention plan is designed Forms of FBA Functional Behavior Analysis Indirect FBA Direct descriptive FBA Indirect FBA often includes A review of records Behavior rating scales Adaptive Behavior Scales, Academic Assessments and Social Skills Assessments Interviews Steps in a Direct FBA Generating an operational definition Determining an appropriate behavior recording procedure Observing and recording the behavior Observing and recording the associated antecedent and consequent variables Key characteristics of functional analysis Focus on overt behaviors of applied (social or clinical) significance Assess behavior through direct observation to identify patterns Use environmental events to influence the behavior Identify, evaluate and demonstrate the factors responsible for behavior change Characteristics of a functional analysis Reflects a way of understanding behavior and using causal information to identify effective interventions Goal is to identify the conditions that control the occurrence and maintenance of behavior by determining the function or purpose that the behavior serves Observing and recording behavior Starts with an operational definition Defining and recording behavior is a two step process Focus on identifying observable behavior or the relevant characteristics displayed by the student Direct observations of the student Choice of Measurement Procedures Frequency recording Duration recording Interval recording Three types Whole interval Partial interval Momentary Time Sampling Permanent Product Recording Playcheck recording Stages of Acting Out Behavior Peak Agitation Trigger Recovery Calm Going beyond the immediate environment Often, students are upset about events outside the immediate setting which makes them more vulnerable to acting out in the setting even though that’s not what really set the behavior problem in motion These are called “setting events” Without having some idea of the influences on the student’s life outside of school the likelihood that one’s inschool BIP will be effective is not good, particularly for more extreme types of behavior “No person is an island” Microsystem Mesosystem Exosystem Microsystem Family Friends Classes School Mesosystem Interaction of student with various microsystems Interactions of microsystems with each other Exosystem Indirect effects on student by decisions/settings that have an impact on his/her life Building a behavioral-ecological model of behavior Thinking outside the box! Behavior What the person does and the extent to which this represents a match or a mismatch between the person and the expectations placed on that person either overtly or subtly by his/her surroundings “The Winner” Norman Rockwell Saturday Evening Post, May 23, 1953 Person Variables Developmental level Cultural, racial, ethnic, gender roles Learning style Learning history Sensitivity to stimulation Resilience and/or frustration tolerance Disability Nutrition Activity level Reaction to medication Antecedent ObservableProximal/Distant Possible triggering, i.e., setting, events that occur prior to the behavior and that are observable Proximal-occur just prior to the behavior (e.g., called on in class) Distant-occur at other times before the behavior (e.g., an altercation with a peer on the bus) Antecedent CovertProximal/Distant Possible triggering thoughts/feelings that occur prior to the behavior and are not typically observable Proximal-occur just prior to the behavior (e.g., perceive a peer’s disrespect) Distant-Recollections from earlier times prior to the behavior (e.g., remembering something that was said last week that generates anger now) Overt ConsequencesProximal/Distant Possible consequences that follow the behavior and which are observable Proximal-Occur temporally close to the behavior (e.g., student gets out of assignment) Distant-Occur temporally distant to the behavior (e.g., student gets to buy desired item for which s/he has been saving) Covert ConsequencesProximal/Distant Possible thoughts/feelings that occur after the behavior which are typically not observable Proximal-occur just after the behavior (e.g., “Boy, am I stupid”) Distant-Anticipation of consequences that will or may occur as a result of the behavior (e.g., “I’ll probably get grounded for a week if they find out” or “I will violate my parole if I hang with my buddies past curfew”) Putting the pieces of the behavioral-ecological model together AOpd P ACpd CCpd B COpd A Behavioral-Ecological Model of Behavior with all of its parts Micro System The Student’s Family, School, Peers & Neighborhood Mesosystem Interchanges Among student and/or his/her micro system AOpd ACpd P B CCpd COpd Before implementing a behavior change approach Answer the who, what, when, where, why questions Ascertain the communicative function of the behavior Obtain baseline measures of the frequency, intensity and/or duration of the behavior Individual interventions vs. Environmental modifications Too often we use a “shoehorn” approach in dealing with students’ behavioral issues, namely we do things intended to make the student fit what’s available rather than looking at how to make environmental modifications that fit the student. Assimilation vs. Accommodation Individualized behavior intervention plans How Why Where Who What When Who has the behavior that needs to change? The student Others, e.g., classmates, friends, teachers, family, etc. What needs to change? The student’s behavior The environment(s) in which the behavior occurs The behaviors, attitudes, values and/or beliefs of others When? During what timeframe is a change/improvement expected? Are those to be involved in behavior change ready, willing and able during the identified time? Where? Artificial vs. natural situations Why? Because student wants to change Because family and/or others of significance want the student to change To conform to rules/policies of school/society Types of behavior problems for which FBA is most commonly used Behaviors that preclude the teacher from teaching or prevent other students from learning Verbal aggression/abuse or physical aggression/abuse Noncompliance Property destruction General guidelines Is this a personal choice but harmless? Will this be a source of embarrassment or disappointment? Will this be a danger to the person or others? How? Make your best guess as to the function of the behavior Determine where to target your intervention Design the intervention based on your analysis of its function Obtain baseline measures of the target behavior before you initiate the intervention Implement the intervention Monitor its implementation and its effects Adjust as needed ABA is a continual process of developing hypotheses and then testing them If the focus of the intervention is on the individual Methods for increasing desired behaviors Methods for decreasing undesirable behaviors Methods for dealing with out-ofcontrol behaviors, i.e., crisis management Methods for increasing desired behaviors Positive reinforcement/negative reinforcement Behavioral contracts Token economy Premack Principle Karan Principle Modeling the desired behaviors Covert approaches Professional Counseling In the moment counseling, i.e., incidental counseling or teaching moment Video clip http://www.youtube.com/watc ?v=92EowaMhXyU Methods for decreasing undesirable behavior Extinction Response cost Negative consequences Time out Overcorrection Covert approaches Thought stopping Covert negative self-statements Professional counseling In the moment counseling, i.e., incidental counseling or teaching moment Self-Management Techniques Self-monitoring Self-assessment Self-reinforcement and selfpunishment Self-control training Biofeedback Cognitive therapies Rational-emotive therapy Covert conditioning Exposure treatments Maintenance, Generalization and Transfer of Training Altering the frequency of rewards Programming naturally occurring reinforcers, e.g., natural consequences Fading the contingencies Expanding the stimulus control Duration of the intervention Shifting to self-management methods Methods for dealing with out-of-control behaviors, i.e., crisis management Ignoring Redirecting Feedback Instructions Active Listening Stimulus change Inter-positioning Physical management Issues, Flaws and Considerations Be tuned into your own emotions to determine whether the behaviors of concern are violating your principles and/or pushing your buttons Try to be objective and functional rather than emotional and reactive, Just because it feels right to you does not mean it is Try to act therapeutically and not react emotionally Don’t be afraid to lose battles and keep your eye on the bigger picture Should not be about winning or losing and it should never be about who has more power Issues, Flaws and Considerations Punishment only teaches a child what not to do, it doesn’t teach him/her what to do Often leaves child feeling the desire for revenge Medication may be helpful but one must remember that even though the student’s problem behavior may only occur for a relatively small percentage of the child’s day the medication is in his/her bloodstream 24 hours a day Are you aware of the effect your communication style may be having on the student? Issues, Flaws and Considerations Is the student’s disability contributing to the behavior? The more intense the student’s behavior the more likely it will be perceived as problematic even if it doesn’t occur very often If the student was your relative would you be comfortable with the approach and believe it to be in your relative’s best interests? Have your earned the right to design an intervention by knowing the student and the student’s situation well enough The biggest flaws with most behavior intervention plans Unrealistic expectations Much too complicated (need to “Keep it simple stupid” or KISS) Blaming the victim Not being correctly implemented Not being monitored or evaluated and changed accordingly as needed There are no cookbooks Every situation/child is different Function over form Above all else, do no harm Plan with your head not your emotions