* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download weiten6_PPT16
Social dilemma wikipedia , lookup
Belongingness wikipedia , lookup
Group development wikipedia , lookup
Carolyn Sherif wikipedia , lookup
Interpersonal attraction wikipedia , lookup
Implicit attitude wikipedia , lookup
Introspection illusion wikipedia , lookup
Human bonding wikipedia , lookup
Group polarization wikipedia , lookup
Interpersonal relationship wikipedia , lookup
Albert Bandura wikipedia , lookup
Group dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Impression formation wikipedia , lookup
Communication in small groups wikipedia , lookup
Social loafing wikipedia , lookup
Social tuning wikipedia , lookup
Attitude (psychology) wikipedia , lookup
False consensus effect wikipedia , lookup
Attitude change wikipedia , lookup
Self-perception theory wikipedia , lookup
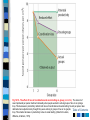
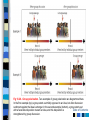
Chapter 16 Social Behavior Social Psychology Person perception Attribution processes Interpersonal attraction Attitudes Conformity and obedience Behavior in groups Table of Contents Person Perception: Forming Impressions of Others Effects of physical appearance Cognitive schemas Stereotypes Prejudice and discrimination Subjectivity in person perception Evolutionary perspectives Table of Contents Fig 16.1 – Examples of social schemas. Everyone has social schemas for various “types” of people, such as sophisticated professionals or working-class stiffs. Social schemas are clusters of beliefs that guide information processing. Table of Contents Attribution Processes: Explaining Behavior Attributions – Internal vs. External – Kelley’s covariation model Biases in attributions – Fundamental attribution error – Defensive attribution – Self-serving bias Cultural influences Table of Contents Fig 16.4 - An alternative view of the fundamental attribution error. According to Gilbert (1989) and others, the nature of attribution processes favor the fundamental attribution error. Traditional models of attribution assume that internal and external attributions are an either-or proposition requiring equal amounts of effort. In contrast, Gilbert posits that people tend to automatically make internal attributions with little effort and then may expend additional effort to adjust for the influence of situational factors, which can lead to an external attribution. Thus, external attributions for others’ behavior require more thought and effort, which makes them less common than personal attributions. Table of Contents Close Relationships: Liking and Loving Key factors in attraction – Physical attractiveness – Matching hypothesis – Similarity – Reciprocity – Romantic Ideals Perspectives on love – Hatfield & Berscheid – Passionate vs. Companionate love – Sternberg - Intimacy and commitment – Hazen & Shaver – love as attachment Evolutionary perspectives – Mating priorities Table of Contents Fig 16.7 - Infant attachment and romantic relationships. According to Hazan and Shaver (1987), people’s romantic relationships in adulthood are similar in form to their attachment patterns in infancy, which are determined in part by parental care-giving styles. The theorized relations between parental styles, attachment patterns, and intimate relations are outlined here. (Data for parental care-giving styles and adult attachment styles based on Table of Contents Hazan and Shaver, 1986, 1987; infant attachment patterns adapted from Shaffer, 1985) Attitudes and Attitude Change 3 components – cognitive, affective, and behavioral Factors in changing attitudes – source, message, and receiver Theories of attitude change – Learning theory – Dissonance theory – Self-perception theory – Elaboration likelihood model Table of Contents Fig 16.9 - The possible components of attitudes. Attitudes may include cognitive, affective, and behavioral components, as illustrated here for a hypothetical person’s attitude about gun control. Table of Contents Fig 16.10 - Overview of the persuasion process. The process of persuasion essentially boils down to who (the source) communicates what (the message) by what means (the channel) to whom (the receiver). Thus, four sets of variables influence the process of persuasion: source, message, channel, and receiver factors. The diagram lists some of the more important factors in each category (including some that are not discussed in the text because of space limitations). (Adapted from Lippa, 1994) Table of Contents Fig 16.13 - Design of the Festinger and Carlsmith (1959) study. The sequence of events in this landmark study of counter-attitudinal behavior and attitude change is outlined here. The diagram omits a third condition (no dissonance), in which subjects were not induced to lie. The results in the nondissonance condition were similar to those found in the lowdissonance condition. Table of Contents Fig 16.14 - Bem’s self-perception theory. The traditional view is that attitudes determine behavior. However, Bem stood conventional logic on its head when he proposed that behavior often determines (or causes people to draw inferences about) their attitudes. Subsequent research on attribution has shown that sometimes people do infer their attitudes from their behavior. Table of Contents Yielding to Others: Conformity Conformity – Solomon Asch (1950s) – Classic experiment • Group size • Group unanimity Table of Contents Yielding to Others: Obedience Obedience – Stanley Milgram (1960s) – Controversial landmark experiment – “I was just following orders” • presence of a dissenter Table of Contents Behavior in Groups: The Influence of Other People The bystander effect - Darley and Latane (1968) – Diffusion of responsibility Group productivity and social loafing Decision making in groups Polarization Groupthink Table of Contents Fig 16.19 - The effect of loss of coordination and social loafing on group productivity. The amount of sound produced per person declined noticeably when people worked in actual groups of two or six (orange line). This decrease in productivity reflects both loss of coordination and social loafing. Sound per person also declined when subjects merely thought they were working in groups of two or six (purple Table of Contents line). This smaller decrease in productivity is due to social loafing. (Data from Latané, Williams, & Harkins, 1979) Fig 16.20 - Group polarization. Two examples of group polarization are diagrammed here. In the first example (top) a group starts out mildly opposed to an idea, but after discussion sentiment against the idea is stronger. In the second example (bottom), a group starts out with a favorable disposition toward an idea, and this disposition is Table of Contents strengthened by group discussion. Fig 16.22 - The three potential components of prejudice as an attitude. Attitudes can consist of up to three components. The tricomponent model of attitudes, applied to prejudice against women, would view sexism as negative beliefs about women (cognitive component) that lead to a feeling of dislike (affective component), which in turn leads to a Table of Contents readiness to discriminate against women (behavioral component). Fig 16.23 - Relationship between prejudice and discrimination. As these examples show, prejudice can exist without discrimination and discrimination without prejudice. In the green cells, there is a disparity between attitude and behavior. Table of Contents Fig 16.24 - Bias in the attributions used to explain success and failure by men and women. Attributions about the two sexes often differ. For example, men’s successes tend to be attributed to their ability and intelligence (blue cell), whereas women’s successes tend to be attributed to hard work, good luck, or low task difficulty (green cells). These attributional biases help perpetuate the belief that men are more competent than women. Table of Contents