* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Table of Contents
Introspection illusion wikipedia , lookup
Albert Bandura wikipedia , lookup
Interpersonal relationship wikipedia , lookup
Impression formation wikipedia , lookup
Social tuning wikipedia , lookup
Group dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Interpersonal attraction wikipedia , lookup
Attitude (psychology) wikipedia , lookup
False consensus effect wikipedia , lookup
Attitude change wikipedia , lookup
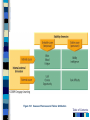
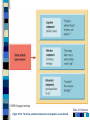
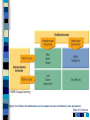
Chapter 16 Social Behavior – 8th Edition Social Psychology Person perception Attribution processes Interpersonal attraction Attitudes Conformity and obedience Behavior in groups Table of Contents Person Perception: Forming Impressions of Others Effects of physical appearance Cognitive/social schemas – Slide 4 Stereotypes Prejudice and discrimination Subjectivity in person perception – Illusory correlation Evolutionary perspectives – Ingroup - outgroup Table of Contents XXXXXX Slide 4 Table of Contents Attribution Processes: Explaining Behavior Attributions – Internal vs. External – Kelley’s covariation model – Attributions in success and failure – Figure 16.1 Biases in attributions – Fundamental attribution error - Figure 16.2 – Defensive attribution – Self-serving bias – credit self for success, blame situation for failure Cultural influences – Individualism – collectivism – Hokotede’s rankings - Figure 16.3 Table of Contents Figure 16.1 Causes of Success and Failure: Attribution Table of Contents XXX16.2 Table of Contents Close Relationships: Liking and Loving Key factors in attraction – – – – – Perspectives on love – – – – Physical attractiveness http://www.faceresearch.org/demos/average Matching hypothesis Similarity, Reciprocity Romantic Ideals Hatfield & Berscheid – Passionate vs. Companionate love Sternberg – Intimacy, commitment, & passion – Figure 16.4 Hazen & Shaver – love as attachment - Figure 16.5 Attachment styles – attachment anxiety/avoidance – F 16.5 Evolutionary perspectives – Mating priorities – Mate poaching – Buss Internet and close relationships – F 16.7 Table of Contents Facial Averaging and Physical Attractiveness Instructions and Background This is a little demonstration in which you generate several examples of average faces from the several that are given at this web address: http://www.faceresearch.org/demos/average 1. Click on any four female or male faces, and form your impression of the attractiveness of the composite (average) face. 2. Press "reset." Now click on any ten female or male faces, and form your impressions now. 3. Do it one more time; this time using a very large number of faces to make your composite. 4. You should observe increasing attractiveness the more faces are used to form your composite face. 5. I hope you had fun with this. Table of Contents Figure 16.4 – Sternberg’s view of love over time Figure 16.5 XXX Table of Contents Attitudes and Attitude Change 3 components – cognitive, affective, and behavioral – Figure 16.8 Factors in changing attitudes – persuasion – source, message, channel, and receiver – Figure 16.9 Theories of attitude change – Learning theory • Classical conditioning and advertising – Figure 16.10 – Dissonance theory – Festinger & Carlsmith (1959) – Figure 16.11 – Self-perception theory – Figure 16.12 – Elaboration likelihood model – Figure 16.13 Table of Contents Figure 16.8 – Components of Attitudes Table of Contents XXX16.9 Table of Contents Figure 16 - 10 Classical conditioning of attitudes in advertising Table of Contents Figure 16.11 xxxxx Table of Contents Figure 16.12 Bem’s selfperception theory Figure 16.13 Elaboration likelihoood model Table of Contents Yielding to Others: Conformity Conformity – Solomon Asch (1950s) – Group norm behavior – Classic experiment - Figure 16.14 • Group size – increased conformity until 4 in incorrect group then level, Figure 16.15 • Group unanimity Compliance – Conforming to requested behavior • Foot-in-door • Door-in-the-face Table of Contents Yielding to Others: Obedience Obedience – Stanley Milgram (1960s) – Controversial landmark experiment – Figure 16.16 • 65% gave highest shock level • Many variations of basic experiment – “I was just following orders” • presence of a dissenter Table of Contents Behavior in Groups: The Power of the Situation Social Roles Stanford Prison Study – p. 692-693 http://www.prisonexp.org/ Table of Contents Behavior in Groups: The Influence of Other People The bystander effect - Darley and Latane (1968) – Diffusion of responsibility Group productivity and social loafing – Figure 16.17 Decision making in groups Group Polarization - Figure 16.18 Groupthink – Bay of Pigs – NASA Shuttle disaster Table of Contents Figure 16.17 XXXXXX Table of Contents Figure 16.18 XXXXXX Table of Contents Understanding Prejudice Prejudice as an attitude – Figure 16.19 Prejudice and discrimination – Figure 16.20 Bias attribution of success and failure – Figure 16.21 Group competition – Sherif et al. (1961) study – field experiment Ingroups and outgroups Threats to social identity – Figure 16.22 Table of Contents Table of Contents Figure 16.19 The three potential components of prejudice as an attitude Figure 16.20 Relationship between prejudice and discrimination Table of Contents Figure 16.21 Bias in the attributions used to explain success and failure by men and women Table of Contents