* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cellular Movement
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
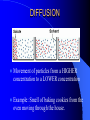
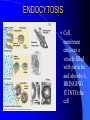
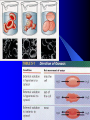
Cellular Movement Passive and Active Transport Passive Transport Does NOT require ENERGY to move particles into or out of a cell Movement of particles from HIGHER concentration to LOWER concentration DIFFUSION – movement of particles OSMOSIS – movement of water DIFFUSION Movement of particles from a HIGHER concentration to a LOWER concentration Example: Smell of baking cookies from the oven moving through the house. OSMOSIS Movement of WATER from a HIGHER concentration to a LOWER concentration Example: Plant taking in water during a rainy day. Active Transport Requires ATP ENERGY to move particles into or out of cell Movement of particles from LOWER concentration to HIGHER concentration Endocytosis Exocytosis ENDOCYTOSIS Cell membrane encloses a vesicle filled with particles and absorbs it, BRINGING IT INTO the cell EXOCYTOSIS Cell membrane encloses a vesicle filled with particles and PUSHES IT OUT of the cell Active Transport Example: A person trying to squeeze into an already crowded elevator! It takes ENERGY to do so! Equilibrium In all cases, cells want EQUILIBRIUM! Too much (or too little) of a good thing is BAD for the cell! What happens to cells when put in salt water? This is why you do not want to drink salt water when you are lost at sea! Water moves out of the cell to try to reach equilibrium. The cell dries out!