* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Power Point for Lesson 1-3
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
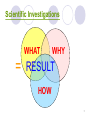
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
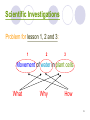
Enhancement of Analytical Thinking through Scientific Investigations Lesson 1, 2, 3 1 Scientific Investigations So many things to consider ! 2 Scientific Investigations What do you want to investigate? (e.g. The mechanism(s) of cell movement…) What is your target study model? (e.g. To study animal? Plant? Bacteria?) What do you want to get from the investigations? (e.g. Any part(s) of the cell that assist(s) cell movement? Mechanisms underlying the observations?) ...... 3 Scientific Investigations “ WHAT ” does matter!!! 4 Scientific Investigations After you have defined a study target (e.g. studying the movement of animal cells), the next question is: Why do you want to investigate such thing? (Significance of your study to the whole picture?) Why do you think your approach will work? Why using such model? ...... 5 Scientific Investigations And then…… executing your plan…… How can you perform the investigation? In this regard, you may need to correlate this with “What” is the expected outcome…… How can you set up the experiment? How long should the investigation be performed? How many samples should I include in the investigation? 6 Scientific Investigations WHAT = WHY RESULT HOW 7 Scientific Investigations The problem is: “ How ” ? 8 Scientific Investigations Qualitative Analysis Vs Quantitative Analysis 9 Scientific Investigations Qualitative Analysis Example: Color of the candy being investigated…… Detect the presence of vitamins inside a kiwi…… The kind of gas being released in a biochemical reaction…… 10 Scientific Investigations Quantitative Analysis Example: The amount of individual color detected in a candy…… The number of vitamin types detected in a kiwi…… The amount of gas released in a biochemical reaction…… 11 Scientific Investigations Problem for lesson 1, 2 and 3: 1 2 3 Movement of water in plant cells What Why How 12 Scientific Investigations Design of Methods/Procedures What to study? Plant cell Study models: potatoes and/or beet root What to study? Movement of water How to study? (Any thing that can “push” water into cells or “pull” water from cells?) Why study movement of water in potatoes and beet root? (e.g. easy to handle? Representative of unspecialized plant cells, etc.) Qualitative Analysis or Quantitative Analysis? 13 Scientific Investigations Think …… 14 Scientific Investigations Hint …… Cells soaked in different concentrations of salt solutions……? Advantages of using potato and beet root……? 15 Scientific Investigations Experimental result ? 16 Scientific Investigations Potato strips soaked in water ? Potato strips soaked in diluted salt solution? Potato strips soaked in concentrated salt solution? Reference link: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Image:Osmotic_pressure_on_blood_cells_diagram.svg 17 Osmosis Movement of water molecules Across the cell membrane which is selectively permeable to different molecules From an area of high water potential (low solute concentration) to an area of low water potential (high solute concentration) A RELATIVE concept of solute concentration 18 Reference links on semi-permeable membrane: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Image:Semipermeable_membrane.png 19 Isotonic solution Hypotonic solution Hypertonic solution (a solution contains same concentration of solute as in another solution) (a solution contains a relatively lower concentration of solute than another solution) solution (a solution contains a relatively higher concentration of solute than another solution) cell Move into the cell Solute (e.g. salt) Tendency of water molecule Move out of the cell Water molecule Osmosis – Biological Importance Cell contains a selectively permeable membrane which allows some solutes to pass through (e.g. water molecule) but not other large molecules (e.g. polysaccharide, large proteins) Osmosis is one of the means that facilitates transport of water in and out of the cell 21 Osmosis – Biological Importance Question: Do you know how guard cell works? 22