* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PROTISTS - SharpSchool
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Chromatophore wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
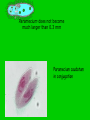
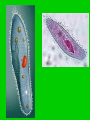
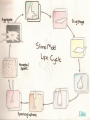
PROTISTS KINGDOMS ARCHAEBACTERIA EUBACTERIA FUNGUS – PROTISTS ANIMAL PLANT WHAT IS A PROTIST? • Organisms that share a lot of characteristics with animals, plants and fungus BUT they cannot be classified in those Kingdoms because of some fundamental differences. • “junk drawer” Kingdom – Very diverse group of organisms • BUT, they do share some characteristics – All are EUKARYOTIC – All live in MOIST SURROUNDINGS THERE ARE THREE TYPES OF PROTISTS • ANIMAL-LIKE (ex. amoeba) • FUNGUS-LIKE (ex. water mold) • PLANT-LIKE (ex. Euglena) ANIMAL-LIKE PROTISTS • Called PROTOZOANS • HETEROTROPHS • Can move from place to place to obtain food. • UNI-CELLULAR • Grouped into four classes based on HOW THEY MOVE PROTOZOANS WITH PSEUDOPODS (sarcodines) What is a pseudopod? -“false foot”; temporary bulges of the cell membrane that fill with cytoplasm May also have a contractile vacuole - collects extra water and then expels it from the cell Example – amoeba AMOEBA Amoebas are unicellular protists that are able to change their shape constantly because their PSEUDOPODS are constantly changing. Pseudopods also help amoebas to get food by ENGULFING and move towards the light. PROTOZOANS WITH CILIA (ciliates) What are cilia?- hair-like projections on cells that move in a wave-like motion. More complex cells, Two nuclei (macro and micro) Oral groove – funnels food into the cell Two contractile vacuoles Example - paramecium Paramecium does not become much larger than 0.3 mm Paramecium caudatum in conjugation PROTOZOANS WITH FLAGELLA (zooflagellates) May have anywhere from 1-8 flagella Most live inside the bodies of other organisms Trypanosoma – carried by Tse Tse flies and infects red blood cells causing the sleeping sickness disease. PROTOZOANS THAT ARE PARASITES (sporozoans) Feed on the cells and body fluids of their hosts. Most do not move, depends on its host to move from place to place; others ooze Plasmodium – does not move; is a parasite; causes malaria Infects a mosquito which then infects a human. FUNGUS-LIKE PROTISTS • • Alike fungus – are HETEROTROPHS, have CELL WALLS, and use SPORES to reproduce Unlike fungus – are able to MOVE at some point in their lives Video FUNGUS-LIKE PROTISTS • Live in moist places, the water, or dead and decaying trees • Brightly colored TYPES OF FUNGUS-LIKE PROTISTS • Water molds • Downey mildews • Slime molds Water molds can be parasitic as seen here. PLANT-LIKE PROTISTS • • • • • Called algae All are AUTOTROPHS Play an important role as a food source in the food chain Provide most of the atmosphere’s oxygen Contain pigments – - Chemicals that produce color ALGAE CHARACTERISTICS • Algae vary greatly in size – Unicellular – Multi-cellular – Colonies • Ex. Volvox These Volvox live in colonies. Even though they are each an individual organism, some Volvox are specialized to perform certain functions for the colony like respiration or reproduction. Gametes Daughter cells Euglenoids • Example: Euglena • Green, uni-cellular algae • Eyespot near the flagella senses light. EUGLENA • Euglenoids, like this Euglena, have the ability to lose their chloroplasts. If you would keep Euglena in the dark they start feeding on organic matter and may loose their pigment Dinoflagellates • Very colorful • Some even fluoresce and can seem to make the ocean “glow” when they are disturbed by waves or passing boats. • Have two flagella and move like spinning tops Diatoms • Found in two basic shapes: – Centric – cylindrical – Pennate – long, oval-shaped • Diatoms are delicate unicellular organisms that have a yellow-brown chloroplast that enables them to photosynthesize. • Their cell walls are made of silica almost like a glass house • Layers of dead diatoms form diatomaceous earth. • Used to make polish, in pool filters and as an insecticide Red and Brown Algae • Almost all red algae • Almost all brown algae is seaweed. is seaweed. • Carrageenan is found in• red algae and is used in ice cream and hair products. Have lots of plant characteristics like holdfasts (roots), blades (leaves) and stalks (stems) Red algal bloom Stalk Green Algae Ex. Spirogyra In Spirogyra the chloroplast runs through the cell like a helix. Protists and Evolution • Protozoans are believed to be the evolutionary ancestors of all forms of animal life. • Green algae are believed to be the evolutionary ancestors to all forms of plant life.