* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Psychology
Reactive attachment disorder wikipedia , lookup
Schizoid personality disorder wikipedia , lookup
Obsessive–compulsive personality disorder wikipedia , lookup
Emergency psychiatry wikipedia , lookup
Kleptomania wikipedia , lookup
Obsessive–compulsive disorder wikipedia , lookup
Personality disorder wikipedia , lookup
Major depressive disorder wikipedia , lookup
Autism spectrum wikipedia , lookup
Excoriation disorder wikipedia , lookup
Glossary of psychiatry wikipedia , lookup
Selective mutism wikipedia , lookup
Bipolar II disorder wikipedia , lookup
Bipolar disorder wikipedia , lookup
Pyotr Gannushkin wikipedia , lookup
Conversion disorder wikipedia , lookup
Antisocial personality disorder wikipedia , lookup
Depersonalization disorder wikipedia , lookup
Mental status examination wikipedia , lookup
Asperger syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Dissociative identity disorder wikipedia , lookup
Conduct disorder wikipedia , lookup
Schizoaffective disorder wikipedia , lookup
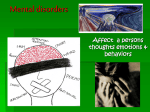
Mental disorder wikipedia , lookup
Panic disorder wikipedia , lookup
History of psychiatry wikipedia , lookup
Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders wikipedia , lookup
Abnormal psychology wikipedia , lookup
Narcissistic personality disorder wikipedia , lookup
Classification of mental disorders wikipedia , lookup
Causes of mental disorders wikipedia , lookup
Spectrum disorder wikipedia , lookup
Depression in childhood and adolescence wikipedia , lookup
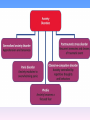
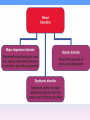
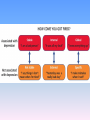
Anxiety disorder wikipedia , lookup
Child psychopathology wikipedia , lookup
History of mental disorders wikipedia , lookup
Thinking About Psychology: The Science of Mind and Behavior Charles T. Blair-Broeker Randal M. Ernst Module 28 Anxiety and Mood Disorders Module 28: Anxiety and Mood Disorders Anxiety Disorders Anxiety and Anxiety Disorders • Anxiety: A vague feeling of apprehension or nervousness • Anxiety disorder: where anxiety begins to take control and dominate a person’s life Types of Anxiety Disorders • Anxiety disorders are divided into: – Generalized Anxiety Disorder – Panic Disorder – Phobia – Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder – Posttraumatic Stress Disorder Module 28: Anxiety and Mood Disorders Anxiety Disorders: Generalized Anxiety Disorder and Panic Disorder Generalized Anxiety Disorder • An anxiety disorder characterized by disruptive levels of persistent, unexplained feelings of apprehension and tenseness Symptoms of Generalized Anxiety • Must have at least three of the following: – Restlessness – Feeling on edge – Difficulty concentrating/mind going blank – Irritability – Muscle Tension – Sleep Disturbance Panic Disorder • An anxiety disorder characterized by sudden bouts of intense, unexplained panic • Panic attacks may happen several times a day Module 28: Anxiety and Mood Disorders Anxiety Disorders: Phobia Phobia • An anxiety disorder characterized by disruptive, irrational fears of specific objects or situations • The fear must be both irrational and disruptive. Phobias Social Phobia • Phobias which produce fear in social situations • Fear of speaking in public Agoraphobia • Fear of situations the person views as difficult to escape from • Fear of leaving one’s home or room in the house Phobia • Play “Three Anxiety Disorders” (4:08) Segment #37 from Psychology: The Human Experience. • The segment includes a discussion on Generalized Anxiety Disorder. Module 28: Anxiety and Mood Disorders Anxiety Disorders: ObsessiveCompulsive Disorder Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder • An anxiety disorder characterized by unwanted, repetitive thoughts and actions • Obsessions – repetitive thoughts • Compulsions – repetitive actions • The obsessions/compulsions begin to take control of the person’s life. Obsessive Compulsive Disorder http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Rn1OYlYzgm8 http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ETFQ9fyRP0s http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8dR8xVqSfXc Module 28: Anxiety and Mood Disorders Anxiety Disorders: Posttraumatic Stress Disorder Posttraumatic Stress Disorder • An anxiety disorder characterized by reliving a severely upsetting event in unwanted recurring memories (flashbacks) and dreams Module 28: Anxiety and Mood Disorders Anxiety Disorders: Causes of Anxiety Disorders Biological Factors • Hereditary factors may result in a predisposition for developing anxiety disorders • Brain functions appear to be different in an anxiety disorder patient • Evolutionary factors may lead to anxiety disorders. Learning Factors • Through classical conditioning people may associate fear with an object. • Observational learning--watching another experiencing fearfulness--may result in developing fear. • Fear of an object may be reinforced when by avoiding the feared objects. Module 28: Anxiety and Mood Disorders Mood Disorders Mood Disorders • Classification of disorders where there is a disturbance in the person’s emotions • Major types of mood disorders include: – Major Depressive Disorder – Bipolar Disorder – Dysthymic Disorder Mania • Period of abnormally high emotion and activity Depression • Extended period of feeling sad, listless, and drained of energy Module 28: Anxiety and Mood Disorders Mood Disorders: Major Depressive Disorder Major Depressive Disorder • A mood disorder in which a person, for no apparent reason, experiences at least two weeks of depressed moods, diminished interest in activities, and other symptoms, such as feelings of worthlessness Dysthymic Disorder • Similar to major depressive disorder but less severe and shorter in duration Module 28: Anxiety and Mood Disorders Mood Disorders: Bipolar Disorder Bipolar Disorder • A mood disorder in which the person alternates between the hopelessness of depression and the overexcited and unreasonably optimistic state of mania • Used to be called manic-depressive disorder • Many times will follow a cyclical pattern Mood Disorders • Play “Mood Disorders: Major Depression and Bipolar Disorder” (4:45) Segment #38 from Psychology: The Human Experience. Mania and Depression • Play “Mood Disorders: Mania and Depression” (7:34) Segment #31 from The Mind: Psychology Teaching Modules (2nd edition). Module 28: Anxiety and Mood Disorders Mood Disorders: Causes of Mood Disorders Biological Factors • Mood disorders have a hereditary nature to them. • Depressed individuals tend to have depressed brains. – PET scans indicate less activity during periods of depression. Major Depressive Episode http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=DiUhn ub6DKo Social-Cognitive Factors • Depression may be a variation of learned helplessness. • Depressed individuals attribute events using the following characteristics: – Stable: the bad situation will last for a long time – Internal: they are at fault – Global: all of life is bad The End