* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download “Connecting to the Disconnected” (Workshop
Rumination syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Mental health professional wikipedia , lookup
Community mental health service wikipedia , lookup
Posttraumatic stress disorder wikipedia , lookup
Excoriation disorder wikipedia , lookup
Personality disorder wikipedia , lookup
Emergency psychiatry wikipedia , lookup
Autism spectrum wikipedia , lookup
Deinstitutionalisation wikipedia , lookup
History of psychiatric institutions wikipedia , lookup
Major depressive disorder wikipedia , lookup
Bipolar disorder wikipedia , lookup
Panic disorder wikipedia , lookup
Bipolar II disorder wikipedia , lookup
Glossary of psychiatry wikipedia , lookup
Antisocial personality disorder wikipedia , lookup
Depersonalization disorder wikipedia , lookup
Conversion disorder wikipedia , lookup
Controversy surrounding psychiatry wikipedia , lookup
Conduct disorder wikipedia , lookup
Anxiety disorder wikipedia , lookup
Mental status examination wikipedia , lookup
Schizoaffective disorder wikipedia , lookup
Asperger syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Dissociative identity disorder wikipedia , lookup
Pyotr Gannushkin wikipedia , lookup
Narcissistic personality disorder wikipedia , lookup
Spectrum disorder wikipedia , lookup
Separation anxiety disorder wikipedia , lookup
Generalized anxiety disorder wikipedia , lookup
Mental disorder wikipedia , lookup
Abnormal psychology wikipedia , lookup
Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders wikipedia , lookup
Depression in childhood and adolescence wikipedia , lookup
Causes of mental disorders wikipedia , lookup
History of psychiatry wikipedia , lookup
Child psychopathology wikipedia , lookup
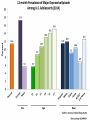
Connecting to the Disconnected The example of Jesus and the demoniac of Gadara in Mark 5 (also Luke 8 and Matthew 8). Mark 5:2-6 • 2 And when he was come out of the ship, immediately there • • • • met him out of the tombs a man with an unclean spirit, 3 Who had his dwelling among the tombs; and no man could bind him, no, not with chains: 4 Because that he had been often bound with fetters and chains, and the chains had been plucked asunder by him, and the fetters broken in pieces: neither could any man tame him. 5 And always, night and day, he was in the mountains, and in the tombs, crying, and cutting himself with stones. 6 But when he saw Jesus afar off, he ran and worshipped him, Mark 5:15 • 15 And they come to Jesus, and see him that was possessed with the devil, and had the legion, sitting, and clothed, and in his right mind: and they were afraid. Mark 5:18-20 • 18 And • 19 Howbeit • 20 And when he was come into the ship, he that had been possessed with the devil prayed him that he might be with him. Jesus suffered him not, but saith unto him, Go home to thy friends, and tell them how great things the Lord hath done for thee, and hath had compassion on thee. he departed, and began to publish in Decapolis how great things Jesus had done for him: and all men did marvel. Mental Health • The prevalence and incidence of mental health disorders is worth reviewing in order to better grasp the size of the population segments affected. • The following summaries are focused on prevalence in adolescents and young adults. ADHD • Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is one of the most common childhood disorders and can continue through adolescence and into adulthood. Symptoms include difficulty staying focused and paying attention, difficulty controlling behavior, and hyperactivity (over-activity). Anxiety Disorders • Anxiety is a normal reaction to stress and can actually be beneficial in some situations. For some people, however, anxiety can become excessive, and while the person suffering may realize it is excessive they may also have difficulty controlling it and it may negatively affect their day-to-day living. There are a wide variety of anxiety disorders, including post-traumatic stress disorder, obsessive-compulsive disorder, and specific phobias to name a few. Collectively they are among the most common mental disorders experienced by Americans. PTSD • Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) is an anxiety disorder that can develop after exposure to a terrifying event or ordeal in which there was the potential for or actual occurrence of grave physical harm. Traumatic events that may trigger PTSD include violent personal assaults, natural or human-caused disasters, accidents, and military combat. People with PTSD have persistent frightening thoughts and memories of their ordeal, may experience sleep problems, feel detached or numb, or be easily startled. Social Phobias • Social phobia is characterized by a persistent, intense, and chronic fear of being watched and judged by others and feeling embarrassed or humiliated by their actions. This fear may be so severe that it interferes with work, school, and other activities and may negatively affect the person’s ability to form relationships. Mood Disorders • Mood disorders represent a category of mental disorders in which the underlying problem primarily affects a person’s persistent emotional state (their mood). The statistics below, derived from the National Comorbidity Survey – Adolescent Supplement (NCS-A) , represent 13 to 17 year olds experiencing major depressive disorder, dysthymic disorder, and/or bipolar disorder. MAJOR DEPRESSION • Major depression is a common mental disorder affecting adolescents in the United States. • The 12-month prevalence data for major depressive episode presented here are from the National Survey on Drug Use and Health (NSDUH). Based mainly on the 4th edition of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-IV), a major depressive episode is defined as: • A period of two weeks or longer during which there is either depressed mood or loss of interest or pleasure, and at least four other symptoms that reflect a change in functioning, such as problems with sleep, eating, energy, concentration, and self- What does this mean for Youth Ministry? • Those who have the most severe cases are often disconnected from others and struggle to develop relationships. • Knowledge and willingness to meet them where they are can allow us to connect with and reach a population that is often simply either not connected to churches or have been ostracized. Q&A