* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Nerve Impulse Notes
SNARE (protein) wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Mechanosensitive channels wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Node of Ranvier wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Action potential wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
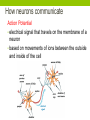
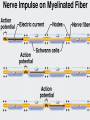
2 Functional Properties of Neurons 1. Irritability • Ability to respond to stimuli 2. Conductivity • Ability to transmit an impulse How neurons communicate Action Potential • electrical signal that travels on the membrane of a neuron • based on movements of ions between the outside and inside of the cell Steps to a Nerve Impulse • Polarized: Resting neuron • Inside membrane is slightly – • Outside membrane is slightly + • Most membrane channels are closed, there is some normal diffusion of K+ or Na+ between cell and the environment through the sodium/potassium pump (active transport) Stimulus Occurs: • Depolarization: Active Neuron • Sodium (Na+) channels open allowing Na+ to diffuse into the cell quickly • This causes the inside to become + (outside -) • Repolarize: Normalizing • K+ gates open in order to allow K+ to diffuse out of the cell – this restores the membrane (+ outside, - inside) Nerve Impulses Figure 7.9a–b • If the stimulus reaches threshold then an action potential is started in the neuron and will travel down the membrane (This is called a nerve impulse) This is the ALL or NONE PRINCIPLE. Nerve Impulses • Refractory Period • K+ must be moved back to the inside of the cell and Na+ must be pumped out of the cell in order to prepare for the next impulse • The sodium-potassium pump ( a membrane channel), using ATP, restores the original configuration Nerve Impulses Figure 7.9e–f Nerve Impulses Figure 7.9c–d Simple Video showing Action Potential • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ifD1YG07fB8 • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7EyhsOewnH4 • http://outreach.mcb.harvard.edu/animations/actionpotenti al_short.swf Long, but good explanation of Action Potential • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-6t_n6kTj1A Transmission of a Signal at Synapses • Impulses are able to cross the synapse to another nerve • Neurotransmitter is released from a presynaptic nerve’s axon terminal http://highered.mcgrawhill.com/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=swf::535::535::/sites/dl/free/00 72437316/120068/bio02.swf::Endocytosis%20and%20Exocytosis • The dendrite of the next neuron has receptors that are stimulated by the neurotransmitter • An action potential is started in the post-synaptic dendrite