* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Spinal Cord - Welcome to Study Windsor
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Anatomy of the cerebellum wikipedia , lookup
Proprioception wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
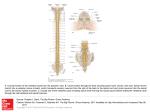
Spinal Cord Runs through the vertebral canal Extends from foramen magnum to second lumbar vertebra Regions Cervical Thoracic Lumbar Sacral Coccygeal Gives rise to 31 pairs of spinal nerves All are mixed nerves Spinal cord Enlargements Cervical enlargement: supplies upper limbs Lumbo -sacral enlargement: supplies lower limbs Conus medullaris- tapered inferior end Ends between L1 and L2 Spinal Segments & Roots Spinal segment C8, T12, L5, S5, Cx1 Anterior (Ventral) Root Posterior (Dorsal) Root Dorsal Root (Spinal) Ganglion Root - Rootlets Spinal Segments Importance of the spinal segments Coverings of Spinal cord Dura mater: outermost layer; continuous with epineurium of the spinal nerves Arachnoid mater: thin and web like Pia mater: bound tightly to surface Ligamentum Denticulatum Cordotomy Forms the filum terminale anchors spinal cord to coccyx Spaces Epidural: external to the dura Anesthestics injected here Epidural Anesthesia Subdural space: serous fluid Subarachnoid: between pia and arachnoid Filled with CSF Coverings of Spinal cord cont… Lumbar Puncture Lumbar Puncture – lumbar (terminal) cistern Spinal Cord White Matter Anterior Funiculus (Anterior White Column) Posterior Funiculus (Posterior White Column) Lateral Funiculus (Lateral White Column) Gray Matter Anterior Horn ------------ motor Posterior Horn -------------- sensory Lateral Horn -----------------autonomic (sympathetic) Gray Commissure -------- anterior and posterior Cord Organization Principles of Cord Organization 1) Longitudinal Arrangement Fibers (White Matter) ------------ White Column Cell Groups (Gray Matter) ------- Gray Column 2) Transverse Arrangement Afferent & Efferent Fibers Crossing (Commissural and Decussating) Fibers 3) Somatotopical Arrangement Somatosensory Pathway(Dorsal Colum) Somatosensory Pathway Posterior column pathway carries sensation of highly localized touch, pressure, vibration. Posterior column pathway includes: Fasciculus cuneatus tract Fasciculus gracilus tract Carries fine touch, pressure, vibration, sterognosis and conscious Proprioceptive sensations. Dorsal Colum tracts dorsal cloumn pathway Dorsal Colum Lesion Left spinal cord injury dorsal column pathway Loss of sense of: •touch •proprioception •vibration in left leg Dorsal Colum Lesions Sensory ataxia Patient staggers; cannot perceive position or movement of legs Visual clues help movement Rombergism Assessment of Dorsal Colum Case …. An 85-year-old man is being evaluated for gait difficulties. On examination it is found that joint proprioception is absent in his toes. People with impaired position sense will usually fall if they stand with their feet together and do which of the following? Flex the neck Extend their arms in front of them Flex the knees Turn the head Close their eyes Clinical Case A 45 year old woman complained of pain in her right breast and progressive weakness of her right lower limb for a period of two months, she contacted her Family physician, Her Family physician referred her to a neurologist. The neurologic evaluation revealed weakness in the right lower limb. This was associated with spasticity (increased tone), hyperreflexia (increased deep tendon reflexes) at the knee and ankle, which also demonstrated clonus. On the right side there was loss of two-point discrimination, touch ,vibratory sense and proprioception at levels below the hip. The left side showed a loss of pain and temperature sensation below dermatome T-7. Clinical Case Of Spinal Cord cont.. MRI of a patient indicated to have an extramedullary tumor expanding from the dorsal roots at spinal cord levels T-5,6. Based on the symptoms and clinical findings what is your diagnosis ? Anterolateral system The Anterolateral Pathway Provides sensations of “crude” touch, pressure, pain, and temperature Ascend within the anterior or lateral spinothalamic tracts: What is Pain? “An unpleasant sensory & emotional experience associated with actual or potential tissue damage, or described in terms of such damage” – Subjective sensation Pain Perceptions – based on expectations, past experience, anxiety, suggestions Affective – one’s emotional factors that can affect pain experience Behavioral – how one expresses or controls pain Cognitive – one’s beliefs (attitudes) about pain Physiological response produced by activation of specific types of nerve fibers Experienced because of nociceptors being sensitive to extreme mechanical, thermal, & chemical energy. Composed of a variety of discomforts One of the body’s defense mechanism (warns the brain that tissues may be in jeopardy) Where Does Pain Come From? Cutaneous Pain – sharp, bright, burning; can have a fast or slow onset Deep Somatic Pain – stems from tendons, muscles, joints, periosteum, & b. vessels Visceral Pain – originates from internal organs; diffused @ 1st & later may be localized (i.e. appendicitis) Psychogenic Pain – individual feels pain but cause is emotional rather than physical Anterolateral System (Pain &Temp) spinothalamic pathway Left spinal cord injury Loss of sense of: •Touch •Pain •Warmth/cold in right leg Spinothalamic Tracts Located lateral and ventral to the ventral horn Carry impulses concerned with pain and thermal sensations (lateral tract) and also non- discriminative touch and pressure (medial tract) Fibers of the two tracts are intermingled to some extent In brain stem, constitute the spinal lemniscus Fibers are highly somatotopically arranged, with those for the lower limb lying most superficially and those for the upper limb lying deeply Lateral Spinothalamic Tract Carries impulses concerned with pain and thermal sensations. Axons of 1st order neurons terminate in the dorsal horn Axons of 2nd order neuron (mostly in the nucleus proprius), decussate within one segment of their origin, by passing through the ventral white commissure & terminate on 3rd order neurons in ventral posterior nucleus of the thalamus Thalamic neurons project to the somatosensory cortex Anterior Spinothalamic Tract Carries impulses concerned with non- discriminative touch and pressure Axons of 1st order neurons enter cord terminate in the dorsal horn Axons of 2nd order neuron (mostly in the nucleus proprius) may ascend several segments before crossing to opposite side by passing through the ventral white commissure & terminate on 3rd order neurons in ventral posterior nucleus of the thalamus Thalamic neurons project to the somatosensory cortex Spino-reticulo-thalamic System The system represents an additional route by which dull, aching pain is transmitted to a conscious level Some 2nd order neurons terminate in the reticular formation of the brain stem, mainly within the medulla Reticulothalamic fibers ascend to intralaminar nuclei of thalamus, which in turn activate the cerebral cortex Pain Control Theories Gate Control Theory Endogenous Opiates Theory Phantom Pain Refferd Pain Gate Control Theory Melzack & Wall, 1965 Substantia Gelatinosa (SG) in dorsal horn of spinal cord acts as a ‘gate’ SG cells of Lamina II act as a inhibitory neurons and inhibit “T” cells of lamina IV Larger diameter afferent fibers of touch excite both SG and T cells, Therefore afferent signals of pain sensation from T cells is blocked by stimulation of inhibitory SG cells. Small diameter afferent fibers excite T cells and Inhibit SG cells Therefore Gate is kept Descending Pain Inhibition Descending Pain Modulation (Descending Pain Control Mechanism) Periaqueductal Gray Area (PGA) – release enkephalins Nucleus Raphe Magnus (NRM) – release serotonin The release of these neurotransmitters inhibit ascending neurons Stimulation of the PGA in the midbrain & NRM in the pons & medulla causes analgesia. Endogenous opioid peptides - endorphins & enkephalins Referred Pain? Dermatomal rule Convergence Facilitation Grey Matter Of Spinal cord White Matter Anterior Funiculus (Anterior White Column) Posterior Funiculus (Posterior White Column) Lateral Funiculus (Lateral White Column) Gray Matter Anterior Horn -----------motor Posterior Horn -------------- sensory Lateral Horn ----------------- autonomic (sympathetic) Gray Commissure -------- anterior and posterior Principles of Cord Organization 1) Longitudinal Arrangement Fibers (White Matter) ------------- White Column Cell Groups (Gray Matter) ------- Gray Column 2) Transverse Arrangement Afferent & Efferent Fibers Crossing (Commissural and Decussating) Fibers 3) Somatotopical Arrangement Principles of Cord Organization Lamina of Rexed Lamina I ---------- posteromarginal nucleus Lamina II ---------- substantia gelatinosa of Rolando Lamina III, IV ----- nucleus proprius Lamina V, VI Lamina VII --------- intermediate gray intermediolateral cell column (ILM) Clarke’s column (Nucleus dorsalis) intermediomedial cell column (IMM) Lamina VIII Lamina IX ---------- anterior horn (motor) cell Lamina X ----------- gray commissure Alpha Motor Neurons Motor Unit Motor End Plate Phasic Tonic Muscle Spindle