* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Theories of Evolution
Objections to evolution wikipedia , lookup
Sociocultural evolution wikipedia , lookup
Sexual selection wikipedia , lookup
Unilineal evolution wikipedia , lookup
Creation and evolution in public education wikipedia , lookup
Transitional fossil wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
State switching wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary mismatch wikipedia , lookup
Evidence of common descent wikipedia , lookup
Punctuated equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Natural selection wikipedia , lookup
Evolving digital ecological networks wikipedia , lookup
Acceptance of evolution by religious groups wikipedia , lookup
Paleontology wikipedia , lookup
Catholic Church and evolution wikipedia , lookup
The Descent of Man, and Selection in Relation to Sex wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Theistic evolution wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
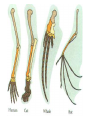
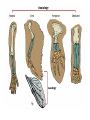
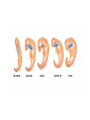
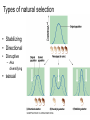
Theories for Evolution Mr. Young Evolution • The process of change within a living system over a period of time • Genotype changes vs. Phenotype changes • Micro vs. Macro Evolution • Many different scientists have proposed theories about this process….… Microevolution: Small-scale evolutionary changes, usually on the molecular level, that occur over the span of a few generations and can therefore be detected in living populations. Macroevolution: Large scale evolutionary changes, speciation events, that may require many hundreds of generations and are usually only detectable in the fossil record Natural Selection: The differential reproductive success of certain phenotypes within a given environment “Survival of the Fittest” Jean Lamarck 1744-1829 “Acquired Traits” • Theory of use and disuse • If an organ is used , it becomes stronger and better developed • If an organ is not used, it becomes weaker and withers away Lamarck • An organism acquires traits from its experience (not genes) and those traits are passed down, or inherited by their offspring • Example: Lamarck believed that giraffes stretched their necks to reach food. Their offspring and later generations inherited the resulting long necks. To Lamarck this means… • If you have a nose job, your kids will inherit the new nose! • In real life, what nose will your kids get? (the old one or the new one?) • Answer: the old one! Is this logical? • What determines that traits are passed to their children? – DNA • If you change your appearance, will your children inherit the new appearance – No, because your DNA did not change Natural Selection • Environmental Selection • Role of the Environment • Acquired traits???? (Lamarck) Who’s Your Daddy? • Charles Darwin – Theory-descent w/ modification – Theory-natural selection-main principles: Charles Darwin 1809 - 1882 • A naturalist (studied and preserved biological specimens that he collected) • 5 year voyage around the world aboard the HMS Beagle Charles Darwin • Theory of evolution by natural selection – Nature will select the organisms that have variations that allow them to better survive (survival of the fittest) – Descent by Modification – Darwin collected different species that were very similar and hypothesized that they shared a common ancestor insects finches Darwin’s Book: Origin of Species by Natural Selection • Described his theory of evolution • Caused a lot of controversy and angered the church • The church initially believed that evolution is a sin against God • Before Darwin died, the church accepted his theory and he was buried in a famous church in England Charles Darwin • Darwin’s theories are accepted today as the most accurate explanation for evolution Darwin explains why giraffes have longer necks than their ancestors • • • • • Overproduction – too many giraffes Struggle or compete for food Variation in length of neck exists naturally Longer neck…reach food...survive Longer necked giraffes survive and reproduce to eventually originate a new species of giraffes Hugo De Vries • Added the concept that mutations in DNA are what cause organisms to change or have variations • Evolution is changes in DNA that is then inherited (microevolution) Variations in organisms • Each species has organisms with varying characteristics for example: – – – – – some are taller some have bigger feet some run faster some have better vision some smell better Struggle for existence • Overproduction of a species causes competition for resources to survive – – – – food water shelter space Survival of the fittest by means of natural selection • Variations may give certain organisms advantages to survive, while other organisms died • Nature selects those organisms that will die or survive Evidence for Darwin's theory • Fossil record • Biogeography • Comparative Anatomy –Embryology –Biochemistry Evidence for Evolution Homologous structures • • • • Similar shape Different function Shared origin Example: arms of human, wings of bats, wings of penguins, arms of alligators • Divergent evolution Evidence for Evolution Analogous structures • • • • Different shape Similar function Different origins Example: wings of a humming bird and wings of a moth, both allow the organism to hover • Convergent evolution Vestigial Structures • A structure that had a use in an ancestor but has no use in a particular organism • Examples: – Appendix in humans – Tail bones in humans… we have no tails – Tiny leg bones in snakes…they have no legs – Wings in penguins…they do not fly – Nipples on boys…they do not produce milk Embryology • The study of an organism from creation to birth • Embryos have – tails that vanish into their spines – gill slits, like fish to breath that vanish into ears – coats of hair that fall off at birth Embryos go through stages of heart development • 2 chambers like fish hearts • 3 chambers like reptiles • 4 chambers like birds and mammals Adaptations • A trait that increases an organisms chances of survival What forces cause evolution? 1. Mutation 2. Migration (gene flow) 3. Genetic drift – Random events – Small populations 4. Non-random mating 5. Natural selection-4 types; Types of natural selection • Stabilizing • Directional • Disruptive – Aka diversifying • sexual Natural Selection? • What leads to these changes? – Random mutations • Organisms w/ shorter generation times have higher mutation rates & so evolve quicker than animals w/ longer generation times • Examples: • Industrial Revolution vs. Peppered Moth Natural selection results from Selection Pressures • those aspects of the environment that can have a notable impact on the reproduction of members of a particular species over evolutionary time. • adaptations Defense Mechanism • Different ways for organisms to defend themselves • Example: thorns on rose bush Mimicry • Copying the appearance of another, more dangerous specie • Example, the fat bumble bees do not sting, but they copy the yellow/black appearance of thin bumble bees that do sting Camouflage • The ability of an organism to blend into their environment • Example, fish have pale bottoms and dark tops • Frogs are shades of green Let’s play name that adaptation!!!