* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slide 1 - s3.amazonaws.com
Tight binding wikipedia , lookup
Probability amplitude wikipedia , lookup
Quantum dot wikipedia , lookup
Quantum fiction wikipedia , lookup
Renormalization group wikipedia , lookup
Quantum computing wikipedia , lookup
De Broglie–Bohm theory wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Wheeler's delayed choice experiment wikipedia , lookup
Quantum entanglement wikipedia , lookup
Topological quantum field theory wikipedia , lookup
Ensemble interpretation wikipedia , lookup
Quantum machine learning wikipedia , lookup
Quantum group wikipedia , lookup
Wave function wikipedia , lookup
Scalar field theory wikipedia , lookup
Quantum field theory wikipedia , lookup
Identical particles wikipedia , lookup
Bell's theorem wikipedia , lookup
Delayed choice quantum eraser wikipedia , lookup
Many-worlds interpretation wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to gauge theory wikipedia , lookup
Elementary particle wikipedia , lookup
Renormalization wikipedia , lookup
Quantum teleportation wikipedia , lookup
Orchestrated objective reduction wikipedia , lookup
Symmetry in quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Quantum key distribution wikipedia , lookup
Electron scattering wikipedia , lookup
Quantum state wikipedia , lookup
Atomic orbital wikipedia , lookup
EPR paradox wikipedia , lookup
Interpretations of quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Electron configuration wikipedia , lookup
Copenhagen interpretation wikipedia , lookup
Quantum electrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Canonical quantization wikipedia , lookup
History of quantum field theory wikipedia , lookup
Double-slit experiment wikipedia , lookup
Bohr–Einstein debates wikipedia , lookup
Matter wave wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
Wave–particle duality wikipedia , lookup
Hidden variable theory wikipedia , lookup
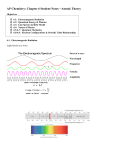
Chapter 7 Quantum Theory of the Atom 7.1 The Wave Nature of Light 7.2 Quantum Effects and Photons 7.3 The Bohr Theory of the Hydrogen Atom 7.4 Quantum Mechanics 7.5 Quantum Numbers and Atomic Orbitals 7.4 Quantum Mechanics Physicists were both mystified and intrigued by Bohr’s theory. They questioned why the energies of hydrogen electron are quantized, or, why is the electron in a Bohr atom restricted or orbiting the nucleus at certain fixed distance? For a decade there is no logical explanation. In 1924, Louis de Broglie provided the solution for this puzzle. If light wave can behave like a stream of particles (photon) then, perhaps particles such as electron can possessed wave properties. De Broglie reasoning led to the conclusion that waves can behave like particles and can exhibit wavelike properties.