* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Power point on the Periodic Table
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
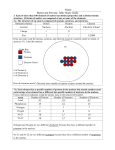
THE PERIODIC TABLE ATOMS Smallest unit of an element that has the properties of that element Basic building blocks of matter Made of protons, neutrons, and electrons ATOMS ARE MADE OF…. Sub-atomic particles! Proton: in the nucleus, symbol “p”, positive charge, much larger mass than an electron Neutron: in the nucleus, symbol “n”, no charge, slightly larger mass than a proton Electron: on shell's around the nucleus, negative charge, symbol “e” Nucleus: dense central core of the atom, contains protons and neutrons IN A NEUTRAL ATOM… Number of protons is equal to number of electrons Number of protons that an atom of any element has is called the atomic number The sum of the protons and neutrons is called the mass number Protons and neutrons make up nearly all the mass of an atom Chemical symbols (e.g. “B”) are used to represent elements Elements are listed in the periodic table by increasing order of atomic number Horizontal rows in the periodic table: period Numbered from 1 to 7 The period also tells you how many shells the element has Vertical columns in the periodic table: group Numbered from 1 to 18 Elements in the same family (group) share similar physical and chemical properties The group also tells you the amount of valence electrons Example Boron Atomic Number Atomic Mass Drawing (with electrons) Finding protons/Neutrons CLASSIFICATION OF ELEMENTS Metals, Non-metals, Metalloids Metals These metals have properties that you normally associate with the metals you encounter in everyday life: They are solid (with the exception of mercury, Hg, a liquid). They are shiny, good conductors of electricity and heat. They are ductile (they can be drawn into thin wires). They are malleable (they can be easily hammered into very thin sheets). All these metals tend to lose electrons easily. Non-metals have properties opposite those of the metals. are brittle not malleable or ductile poor conductors of both heat and electricity tend to gain electrons in chemical reactions. Some non-metals are liquids. Metalloids The elements within the stair-stepped line Have properties that are somewhat of a cross between metals and nonmetals. Have unique conductivity properties (they only partially conduct electricity) SPECIAL GROUPS Some groups have unique names…. Group 1: Alkali metals Group 2: Alkaline earth metals Group 3 – 12: Transition metals Group 17: Halogens Group 18: Nobel gases