* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Seasonal Outlook Briefing
ExxonMobil climate change controversy wikipedia , lookup
Michael E. Mann wikipedia , lookup
Climatic Research Unit email controversy wikipedia , lookup
Soon and Baliunas controversy wikipedia , lookup
Mitigation of global warming in Australia wikipedia , lookup
Heaven and Earth (book) wikipedia , lookup
Global warming controversy wikipedia , lookup
Fred Singer wikipedia , lookup
Climate resilience wikipedia , lookup
Climate change denial wikipedia , lookup
Climate engineering wikipedia , lookup
Politics of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Citizens' Climate Lobby wikipedia , lookup
Climate governance wikipedia , lookup
General circulation model wikipedia , lookup
Economics of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Climate change adaptation wikipedia , lookup
Climate sensitivity wikipedia , lookup
Climatic Research Unit documents wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in Saskatchewan wikipedia , lookup
Global warming wikipedia , lookup
Solar radiation management wikipedia , lookup
Global warming hiatus wikipedia , lookup
Future sea level wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on human health wikipedia , lookup
Carbon Pollution Reduction Scheme wikipedia , lookup
Climate change feedback wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Media coverage of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Global Energy and Water Cycle Experiment wikipedia , lookup
Attribution of recent climate change wikipedia , lookup
Scientific opinion on climate change wikipedia , lookup
Physical impacts of climate change wikipedia , lookup
Public opinion on global warming wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and poverty wikipedia , lookup
Instrumental temperature record wikipedia , lookup
Surveys of scientists' views on climate change wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in Tuvalu wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on humans wikipedia , lookup
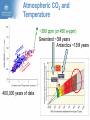
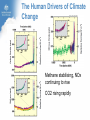
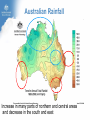
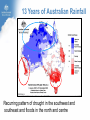
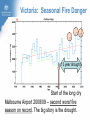
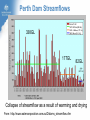
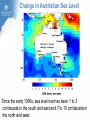
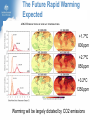
Climate Change and its Effect on Safety and Infrastructure Dr David Jones Head of Climate Analysis & Prediction Bureau of Meteorology Acknowledge: CSIRO, BoM, IPCC, ACE CRC, Dep Climate Change Overview • Why you should care about climate change • Recent Climate Changes (focus on Australia & last 50 years): • Human climate drivers - CO2 (the main GHG) • Temperature • Rainfall • Sea level • Looking to the future of climate change Most of the observed increase in globally averaged temperatures since the mid-20th century is very likely due to the observed increase in anthropogenic greenhouse gas concentrations (IPCC 2007) Atmospheric CO2 and Temperature ~390 ppm (or 450 e-ppm) Greenland ~3M years Antarctica ~13M years 400,000 years of data The Human Drivers of Climate Change Methane stabilising, NOx continuing to rise CO2 rising rapidly Climate Change Impacts – Extremes, Safety and Infrastructure • Direct effects of climate change on individual extreme events: e.g., storms & heatwaves • Indirect (background) effects: e.g., sea level rise exacerbating floods, higher temperatures leading to drying of forest fuels, lower fuel loads (due to winter drying) • Effects on resilience & preparedness: e.g., – Rural depopulation due to drought less fire fighting volunteers? – Uncertain return period for events (leading to over/under investment in preparedness) – Non-availability of insurance or insurance too expensive – Uncertainty delaying or stopping investment decisions – Long-term drought (or perceptions of fire risk) damaging rural economies Australian Temperatures Annual and Decadal Mean Temperature Anomalies For Australia Temperature Anomalies (°C) 1.25 1.00 Decadal mean 0.75 0.50 0.25 0.00 -0.25 -0.50 -0.75 -1.00 -1.25 1960 Departures from 1961-90 normal 1970 1980 1990 Year 2000 2010 Temperature has increased by about 0.7 C since 1960 2005 was Australia’s warmest year on record, 2009 the second warmest Changes in Maximum Temperature Extremes Number in Each Year Distribution of High Maximum Temperatures 60 Decadal mean 50 40 30 20 10 0 1960 1970 1980 1990 2000 Year Highest maximum temperatures tend to occur in recent years, with the largest number on record in 2009 Melbourne: Mortality versus Maximum Temperature Black Saturday (46.4°C) Vic Gov (Aged Care, 2010) Nicholls (2010) Australian Rainfall Increase in many parts of northern and central areas and decrease in the south and east 13 Years of Australian Rainfall Recurring pattern of drought in the southwest and southeast and floods in the north and centre Victoria: Seasonal Fire Danger 13 year drought Start of the long dry Melbourne Airport 2008/09 – second worst fire season on record. The big story is the drought. Perth Dam Streamflows 338GL 177GL 82GL Collapse of streamflow as a result of warming and drying From: http://www.watercorporation.com.au/D/dams_streamflow.cfm Change in Sea Level Global Mean Sea Level (mm) 150 100 50 0 -50 -100 1860 1880 1900 1920 1940 Year 1960 1980 2000 2020 Approximately 20cm since 1870, with a steepening rise Follows very closely global temperatures – a result of thermal expansion and melting of ice Change in Australian Sea Level Since the early 1990s, sea level rise has been 1 to 3 cm/decade in the south and east and 7 to 10 cm/decade in the north and west Infrastructure and Safety Gold Coast, QLD Mandurah, WA Waratah Bay, Vic Some 711,000 addresses are within 3 km of the coast and within 6m of sea level (Engineers Australia) ~3m Impact in the Coastal Zone Increase in the frequency of high sea level events for a 0.5M sea level rise (ACE CRC 2008) Managing our Coastal Zone in a Changing Climate (2009) If sea-levels rose by 0.9 metres, 4700 residential lots along the Lake Macquarie waterway foreshore would be inundated. With almost 250,000 vulnerable coastal buildings,~3m Queensland is at the highest risk from all Australian states... In Vic, more than 80,000 coastal buildings and infrastructure are at risk from the projected sea level rise, coastal flooding and erosion. Projections for Australia in 2030 (CSIRO & BoM) Warmer by 0.4 to 2.0°C 10-50% increase in days over 35°C 10-80% decrease in days below 0°C Up to 10% less annual rainfall in SE Australia Up to 20% less annual rainfall in SW Australia Up to 10% more summer rainfall on east coast Up to 10% more autumn rainfall inland Heavier rainfall where average rainfall increases or decreases slightly Increase in intensity of tropical cyclones The Future Rapid Warming Expected +1.7ºC 600ppm +2.7ºC 850ppm +3.2ºC 1250ppm Warming will be largely dictated by CO2 emissions Emerging Consensus on Rainfall Changes Rainfall change for 2090-2099 relative to 1980-1999. Drying across southern Australia (and indeed most subtropical areas). How Will Changes Appear? • In a country such as Australia where natural climate variability is large, the effects of climate change are more likely to manifest themselves as a series of threshold exceedences leading to stressful events and dislocation followed by (partial) recovery • Climate change will manifest itself through the weather • • • Expect surprises Expect unexpected emergencies and impacts It is not easy (perhaps possible) to link individual events to climate change until the climate change is large In Summary • Data from the Bureau, CSIRO and peer organisations shows a picture of pervasive and consistent trends • The trends are continuing and will have an escalating impact across society – health, safety, infrastructure, planning… • The quality of the data and science is high, and the base data are all available for scrutiny and independent analysis