* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Detection and attribution at the continental scale
Climate change in the Arctic wikipedia , lookup
Michael E. Mann wikipedia , lookup
Heaven and Earth (book) wikipedia , lookup
Climate change denial wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on human health wikipedia , lookup
Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change wikipedia , lookup
German Climate Action Plan 2050 wikipedia , lookup
Climate change mitigation wikipedia , lookup
Climatic Research Unit documents wikipedia , lookup
Low-carbon economy wikipedia , lookup
2009 United Nations Climate Change Conference wikipedia , lookup
Economics of climate change mitigation wikipedia , lookup
Global warming controversy wikipedia , lookup
Climate change adaptation wikipedia , lookup
Fred Singer wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in Tuvalu wikipedia , lookup
Climate governance wikipedia , lookup
Instrumental temperature record wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Climate engineering wikipedia , lookup
Citizens' Climate Lobby wikipedia , lookup
Global warming hiatus wikipedia , lookup
Climate sensitivity wikipedia , lookup
Criticism of the IPCC Fourth Assessment Report wikipedia , lookup
Media coverage of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Economics of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on humans wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming wikipedia , lookup
United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change wikipedia , lookup
Global Energy and Water Cycle Experiment wikipedia , lookup
Mitigation of global warming in Australia wikipedia , lookup
Climate change, industry and society wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in Canada wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and poverty wikipedia , lookup
Attribution of recent climate change wikipedia , lookup
Global warming wikipedia , lookup
Public opinion on global warming wikipedia , lookup
Scientific opinion on climate change wikipedia , lookup
Carbon Pollution Reduction Scheme wikipedia , lookup
Physical impacts of climate change wikipedia , lookup
General circulation model wikipedia , lookup
Solar radiation management wikipedia , lookup
Politics of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Surveys of scientists' views on climate change wikipedia , lookup
Business action on climate change wikipedia , lookup
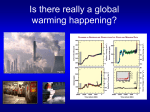
LIVE INTERACTIVE LEARNING @ YOUR DESKTOP NSTA Web Seminar: Earth Then, Earth Now: Our Changing Climate Climate Change Jeopardy Presented by Dr. Mike Winton, NOAA Tuesday, March 31, 2009 Climate Change Jeopardy Host: Mike Winton of NOAA/GFDL 31 March 2009 The categories are • Observations of change • Basic greenhouse physics • Climate models & what they tell us • Climate change options The earth’s surface is warming GISS Temperature The heat that has warmed our climate did not come out of the ocean IPCC Ice is declining globally 1993-2003 sea level rise Antarctica 0.20 mm/yr Greenland 0.21 mm/yr Glaciers and Ice Caps 0.77 mm/yr Total 1.18 mm/yr • Both Greenland and Antarctica are losing ice • Glaciers are retreating globally • Northern hemisphere snow cover has declined • Northern hemisphere sea ice cover is declining • Southern hemisphere sea ice cover is not declining Sea level is rising (ice melt + seawater expansion) IPCC Earth’s energy balance is the key to long-term climate change IPCC Without the greenhouse effect the earth’s climate would be … A) The same B) A wee bit cooler C) Like the ice ages D) Like a big ice ball Without the greenhouse effect the earth’s climate would be … A) The same B) A wee bit cooler C) Like the ice ages D) Like a big ice ball The most important greenhouse gas is? A) N2 (78 % of the atmosphere) B) O2 (21 % of the atmosphere) C) H20 (<1 % of the atmosphere) D) CO2 (0.038 % of the atmosphere) The most important greenhouse gas is? A) N2 (78 % of the atmosphere) B) O2 (21 % of the atmosphere) C) H20 (<1 % of the atmosphere) D) CO2 (0.038 % of the atmosphere) Water vapor is a climate feedback Atmospheric CO2 is increasing Global Warming Art Atmospheric CO2 was stable prior to the 19th century IPCC The CO2 increase is anthropogenic CDIAC We are perturbing the Global carbon cycle IPCC Atmospheric carbon has a range of timescales from short to very, very long Global Warming Art Our greenhouse gas emissions have changed the heat budget of the entire earth by? A) About 0.01 % B) About 0.1 % C) About 1 % D) About 10 % Our greenhouse gas emissions have changed the heat budget of the entire earth by: A) about 0.01 % B) about 0.1 % C) about 1 % D) about 10 % There are numerous anthropogenic forcings of climate change IPCC We need global climate models to help us sort this out but they are … A) Somewhat credible because they are based on fundamental physical and chemical principles B) Not completely reliable since they have significant disagreement with each other C) Both D) Neither We need global climate models to help us sort this out but they are … A) Somewhat credible because they are based on fundamental physical and chemical principles B) Not completely reliable since they have significant disagreement with each other C) Both D) Neither What is a global climate model? A GCM is a mathematical representation of the major climate system components and their interactions. The GCM equations operate on a global grid and are solved on a computer. Atmosphere Land Ocean Concentrations of radiatively active species Emissions of radiatively active species Ice Physical CM ESM* *Earth System Model Climate model equations are solved on global grids Current model resolution 1980s Atmosphere 2 deg. 1990s 2000s OCEAN MODEL RESOLUTION: 1 deg. Simulated vs. Parameterized • Simulated processes: larger than grid-scale, based on bedrock scientific principles (conservation of energy, mass and momentum). Example: storms. • Parameterized processes: smaller than grid scale, formulations guided by physical principles but also make use of observational data. Example: clouds. Detection and attribution of climate change using models (2) Attribution: anthropogenic forcing is that “something” (1) Detection: something beyond natural variability is happening to the global climate IPCC Detection and attribution at the continental scale Climate models need emissions to project future climate change IPCC Projection: 21st century global temperature rises further IPCC The hydrologic cycle intensifies Sea level rises further IPCC Caveat: ice sheet dynamic response not fully modeled Global warming impacts Option 1: Adapt IPCC Option 2: Mitigation stabilize carbon emissions Socolow, Scientific American 2006 • Conserve energy or produce it more efficiently • Use alternative energy: solar, wind, bio, nuclear • Sequester carbon Emissions growth has powerful socio-economic drivers IPCC Emissions growth has powerful socioeconomic drivers The Rich Emissions per capita Rich emission level The Rest Become Rich The Rest Population Pop. increases If we stopped emitting greenhouse gasses the earth would cool back down in? A) 1 year B) 10 years C) 100 years D) 1000 years or longer If we stopped emitting greenhouse gasses the earth would cool back down in A) 1 year B) 10 years C) 100 years D) 1000 years or longer Even if emissions were cut to zero, temperature would fall very slowly Solomon S. et.al. PNAS 2009;106:1704-1709 There are three options: • Mitigation – reduce carbon emissions • Adaptation – adjust to climate change as best we can • Geoengineering (e.g. continuously inject reflective aerosols into stratosphere) What option(s) are best A) Mitigation B) Adaptation C) Mitigation and adaptation, not geoengineering D) Adaptation and geoengineering, not mitigation Summary: Climate change jeopardy is a high stakes game with uncertain odds Basic greenhouse physics CO2 increase anthropogenic Earth is warming Warming is anthropogenic Future carbon emissions Future climate change Impacts of future climate change More certain Less certain Special Thanks to NOAA, SRS and USFS for sponsoring this Web Seminar! http://www.elluminate.com http://learningcenter.nsta.org National Science Teachers Association Dr. Francis Q. Eberle, Executive Director Zipporah Miller, Associate Executive Director Conferences and Programs Al Byers, Assistant Executive Director e-Learning NSTA Web Seminars Paul Tingler, Director Jeff Layman, Technical Coordinator