* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download China -- CAIT briefing - BASIC
Fred Singer wikipedia , lookup
Global warming controversy wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Emissions trading wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on humans wikipedia , lookup
Scientific opinion on climate change wikipedia , lookup
Solar radiation management wikipedia , lookup
Instrumental temperature record wikipedia , lookup
Climate governance wikipedia , lookup
Climate change feedback wikipedia , lookup
Climate change, industry and society wikipedia , lookup
Surveys of scientists' views on climate change wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and poverty wikipedia , lookup
Global warming wikipedia , lookup
Low-carbon economy wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Climate change mitigation wikipedia , lookup
Kyoto Protocol wikipedia , lookup
German Climate Action Plan 2050 wikipedia , lookup
Climatic Research Unit documents wikipedia , lookup
Mitigation of global warming in Australia wikipedia , lookup
Economics of global warming wikipedia , lookup
United Nations Climate Change conference wikipedia , lookup
Paris Agreement wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in New Zealand wikipedia , lookup
Public opinion on global warming wikipedia , lookup
Years of Living Dangerously wikipedia , lookup
2009 United Nations Climate Change Conference wikipedia , lookup
Global Energy and Water Cycle Experiment wikipedia , lookup
Business action on climate change wikipedia , lookup
Economics of climate change mitigation wikipedia , lookup
IPCC Fourth Assessment Report wikipedia , lookup
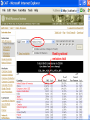
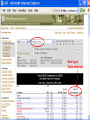
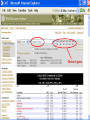
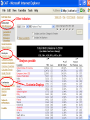
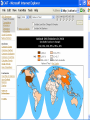
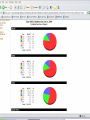
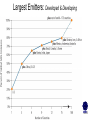
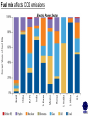
International Climate Policy Post-2012 Quantitative Tools and Negotiating Capacity A Review of WRI’s Climate Analysis Indicator Tool (CAIT) Beijing, China February, 2006 Jonathan Pershing Climate, Energy and Pollution Program World Resources Institute http://www.wri.org WRI What is CAIT? WRI • A web-based information and analysis tool on global climate change developed by The World Resources Institute (WRI). • CAIT includes: – Data on all greenhouse gases (GHGs) and sources, plus other data and indicators relevant to climate change policy – Data for 186 countries (most UNFCCC Parties) and regions – Analysis tools (e.g., trend, sector, or gas analysis) WRI http://cait.wri.org WRI What is CAIT? (2) • Purposes – Promote greater access to information – Support decision-making processes and help build capacity – Provide common platform for data and analysis • Policy neutral • Available free to the public at http://cait.wri.org WRI Acknowledgements • Data providers – – – – – CDIAC RIVM IPCC IEA World Bank – – – – – UNDP U.S. EPA U.S. EIA UNFCCC Houghton • Funding providers • U.S. EPA, Government of Norway, Wallace Global Fund, Prospect Hill Foundation WRI Data – Policy Linkage Working assumptions: – Information is the first step to solving any problem – Better information → better decisions – “Delivery system” matters 1. CAIT 2. Navigating the Numbers report WRI Who is Using CAIT? By Sector 40% 30% 35% 35% 25% 30% 25% 24% 23% 20% 19% 20% 15% 10% 5% 0% Governmental 4% Academia Latin America Asia US + Canada Europe 7% Africa & Mid. East 10% 0% 28% Private Sector & Media By Country/Region NGO/Research ~5000 total users from 108 countries, December 2003 to present WRI Using CAIT CAIT Screens WRI Rank by national emissions total WRI Bottom of the ranking: 186 countries WRI Rank by per Capita emissions WRI Choice of gases WRI Other indicators Analyses possible Customize Displays WRI WRI Choosing Display Regions WRI WRI WRI WRI Vulnerability and Adaptation WRI Some CAIT Results WRI Policy-Relevant Implications • • • • • Global trends Big emitters Emission caps and developing countries Formulaic approaches to commitments Sectoral cooperation WRI Projected Future GHG Emissions Growth % Percent change from 2000 WRI Policy-Relevant Implications • Global trends • Big emitters • Emission caps and developing countries • Formulaic approaches to commitments • Sectoral cooperation WRI Largest Emitters: Developed & Developing WRI Policy-Relevant Conclusions • Global trends • Big emitters • Emission caps and developing countries • Formulaic approaches to commitments • Sectoral cooperation WRI Fixed targets: challenging in the context of massive uncertainty Projected CO2 Emissions Growth to 2025 WRI Policy-Relevant Conclusions • Global trends • Big emitters • Emission caps and developing countries • Formulaic approaches to commitments • Sectoral cooperation WRI Historical Contributions: Major Data Constraints Cumulative CO2 Emissions, Comparison of Different Time Periods WRI Emissions per Capita: Consensus? GHG Emissions per Capita WRI Fuel mix affects CO2 emissions Electric Power Sector WRI Policy-Relevant Conclusions • • • • Global trends Big emitters Emission caps and developing countries Formulaic approaches to commitments • Sectoral cooperation WRI GHG Flow Diagram: Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions WRI International Sectoral Cooperation • Different “forms” of sectoral cooperation • How important is the sector? [% global GHGs] • Underlying rationale for sectoral cooperation – Promote participation – Avoid “leakage” – Promote even regulatory playing field (competitiveness) • Options for international cooperation WRI Conclusions • Global trends are in the wrong direction • Address GHGs in context of big emitting countries and sectors – Int’l cooperation, investment, technology • No single indicator tells a complete story • Data does not point directly toward a solution – Nature and scale of problem – Diverse national circumstances WRI Using CAIT http://cait.wri.org WRI