* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lecture slides from 2007
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
End-plate potential wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
Caridoid escape reaction wikipedia , lookup
Embodied language processing wikipedia , lookup
Electromyography wikipedia , lookup
Proprioception wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Muscle memory wikipedia , lookup
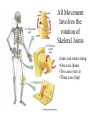
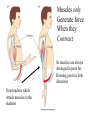
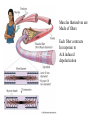
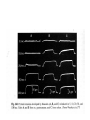
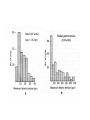
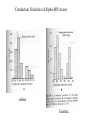
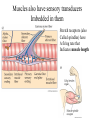
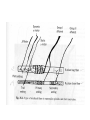
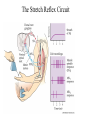
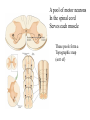
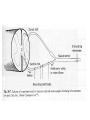
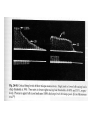
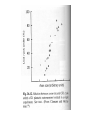
Motor 1 All Movement Involves the rotation of Skeletal Joints Joints can rotate along: •One axis (knee) •Two axes (wrist) •Three axes (hip) Muscles only Generate force When they Contract So muscles are always Arranged in pairs for Rotating joints in both directions Note tendons which Attach muscles to the skeleton Muscles Contract in Response to Acetyl Choline Cholinergic Motor neurons make these connections Muscles themselves are Made of fibers Each fiber contracts In response to Ach induced depolarization Muscle Has Different Fiber Types Cat Gastrocmenius Cat Soleus Contractile Properties of Whole Muscles Vary Muscles Have Heterogenous Properties Twitch Contractions The Motor Unit Motor Units are Homogenous by Fiber Type Fiber Types are Adaptive Conduction Velocities of Alpha-MN Axons soleus Gastroc. The Size Principle Feedback Signals From Muscle Muscles also have sensory transducers Imbedded in them Stretch receptors (also Called spindles) have A firing rate that Indicates muscle length The Stretch Reflex Circuit The Motor Neuronal Pool The Motor-Neuronal Pool A pool of motor neurons In the spinal cord Serves each muscle These pools form a Topographic map (sort of) The Law of Combination -Elwood Henneman