* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Integers Comparing and Ordering
Mathematics of radio engineering wikipedia , lookup
Infinitesimal wikipedia , lookup
Georg Cantor's first set theory article wikipedia , lookup
Positional notation wikipedia , lookup
Abuse of notation wikipedia , lookup
Real number wikipedia , lookup
Law of large numbers wikipedia , lookup
Large numbers wikipedia , lookup
Location arithmetic wikipedia , lookup
Collatz conjecture wikipedia , lookup
Proofs of Fermat's little theorem wikipedia , lookup
Division by zero wikipedia , lookup
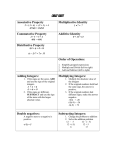
Integers: Comparing and Ordering EQ • How do we compare and order rational numbers? Rational Numbers Rational Numbers Integers Whole Numbers (Positive Integers) Fractions/Decimals Negative Integers Rational numbers •Numbers that can be written as a fraction. Example: 2 = 2 = 2 ÷ 1 = 2 1 Whole Numbers • Positive numbers that are not fractions or decimals. 1 2 3 4 5 6 Integers • The set of whole numbers and their opposites. -7 -6 -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 0 1 2 3 4 5 Positive Integers • Integers greater than zero. 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 Negative Integers • Integers less than zero. -6 -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 0 Comparing Integers • The further a number is to the right on the number line, the greater it’s value. < -1 Ex: -3 ___ -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 . . 0 1 2 3 4 5 -1 is on the right of -3, so it is the greatest. Comparing Integers • The farther a number is to the right on the number line, the greater it’s value. > -5 Ex: 2 ___ -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 . 0 1 2 . 3 4 5 2 is on the right of -5, so it is the greatest. Comparing Integers • The farther a number is to the right on the number line, the greater it’s value. > -2 Ex: 0 ___ -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 . 0 . 1 2 3 4 5 0 is on the right of -2, so it is the greatest. Ordering Integers When ordering integers from least to greatest follow the order on the number line from left to right. Ex: 4, -5, 0, 2 -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 . 0 . 1 2 . 3 Least to greatest: -5, 0, 2, 4 4 . 5 Ordering Integers When ordering integers from greatest to least follow the order on the number line from right to left. Ex: -4, 3, 0, -1 -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 . 0 .. 1 2 3 . Greatest to least: 3, 0, -1, -4 4 5 Try This: < 4 a. -13 ___ b. -4 ___ -7 < < 32 c. -156 ___ d. Order from least to greatest: -9, -3, 5, 15 15, -9, -3, 5 _______________ e. Order from greatest to least: 2, -7, -8, -16 -16, -7, -8, 2 _______________ EQ • How do we find the absolute value of a number? Absolute Value • The distance a number is from zero on the number line. Symbols: |2| = the absolute value of 2 Start at 0, count the jumps to 2. -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 0 1 2 It takes two jumps from 0 to 2. |2| = 2 3 4 5 Absolute Value • The distance a number is from zero on the number line. Ex: |-4| = Start at 0, count the jumps to -4. -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 0 1 2 3 It takes four jumps from 0 to -4. |-4| = 4 4 5 Solving Problems with Absolute Value When there is an operation inside the absolute value symbols; solve the problem first, then take the absolute value of the answer. Ex: |3+4| =|7| =7 Ex: |3|- 2 = 3-2 = 1 Hint: They are kind of like parentheses – do them first! Try This: a. |15| = _____ 15 b. |-12| = _____ 12 13 c. |-9| + 4 = _____ d. |13 - 5| = _____ 8