* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Storage and Retrieval
Limbic system wikipedia , lookup
Source amnesia wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Effects of alcohol on memory wikipedia , lookup
Socioeconomic status and memory wikipedia , lookup
Prenatal memory wikipedia , lookup
Memory and aging wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics in learning and memory wikipedia , lookup
Implicit memory wikipedia , lookup
Sparse distributed memory wikipedia , lookup
Memory consolidation wikipedia , lookup
State-dependent memory wikipedia , lookup
Music-related memory wikipedia , lookup
Atkinson–Shiffrin memory model wikipedia , lookup
Eyewitness memory (child testimony) wikipedia , lookup
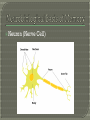
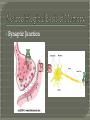
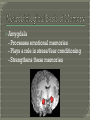
Modules 25-26 Part 1 Raw, unprocessed information Sight, touch, smell, sound, taste Stimuli Changes Selection for further processing Integrates sensory fragments into perception Sensory Memory STM Long Term Memory Listen carefully and write each series of digits on a scrap piece of paper after I finish reciting them. Should have been about 7 digits. May have been slightly higher because recall for random digits is better than random letters. Why might that be? Space is limitless. Genetic? Eidetic Memory Article http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Soxs MMV538U Very complex system MEMORIES DO NOT RESIDE IN SINGLE SPOTS- Equipotentiality Biological Basis Neuron (Nerve Cell) Synaptic Junction http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GMeh TI6DPYI&feature=related Long-Term Potentiation: Strengthened neural firing, creating more permanent pathways for memory. When neurons “fire together”, they “wire together”. Billions of Connections Neural connections that support memory become stronger- Medial Temporal Lobes Library Every Book Analogy time a memory is retrieved and reconsolidated, it changes slightly Memory Short-Term Memory (Working) Long-Term Memory Implicit (Innate) Explicit Semantic (General Knowledge) Episodic (Events) Procedural (Brushing Teeth) Conditioning (Hot Stove) Remembering future time… to do something at some 1. Walking (for an adult) 2. The value of pi to six decimal places 3. Writing a computer program 4. The fact that working memory is brief 5. The fact that you need to drive your sister home from school 6.The fact that the smell of eggs makes you sick and you don’t know why Hippocampus - Processes Explicit Memories - Transfers to other areas for storage -Works with frontal lobe- thinking area Cerebellum - Stores implicit memories -Right above spinal cord - Evolutionarily/Developmentally older Amygdala - Processes emotional memories - Plays a role in stress/fear conditioning - Strengthens these memories Infantile Amnesia: - Learn most reactions/skills during first three years, but we have no explicit memory of these events. This dual system might explain why therapists spent many years investigation the influence of childhood experiences… Permanent effects may be a result of implicit memory, not explicit. Part 2 Seven Dwarfs: List vs. No List Recall: 1. Must List Information/Options 2. Eliminate Wrong Choices Recognition: Only Choices Eliminate Wrong How mnemonics work The word element might trigger the following: Situational Scuba Déjà similarity helps memory experiment vu I’m Really Angry Wow…they were really mean When I was five, my parents yelled at me about organizing my money Remember that time my wallet was stolen I’m angrier How might the mood-congruent theory explain the human experience of good vs. bad days? Karma?