* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Climate Change
Snowball Earth wikipedia , lookup
Soon and Baliunas controversy wikipedia , lookup
Michael E. Mann wikipedia , lookup
Mitigation of global warming in Australia wikipedia , lookup
ExxonMobil climate change controversy wikipedia , lookup
Climate resilience wikipedia , lookup
Economics of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Climatic Research Unit documents wikipedia , lookup
Heaven and Earth (book) wikipedia , lookup
Global warming controversy wikipedia , lookup
Global warming hiatus wikipedia , lookup
Climate change denial wikipedia , lookup
Instrumental temperature record wikipedia , lookup
Fred Singer wikipedia , lookup
Climate change adaptation wikipedia , lookup
Climate governance wikipedia , lookup
General circulation model wikipedia , lookup
Citizens' Climate Lobby wikipedia , lookup
Climate sensitivity wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in Tuvalu wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on human health wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Politics of global warming wikipedia , lookup
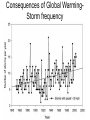
Climate engineering wikipedia , lookup
Media coverage of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Global warming wikipedia , lookup
Physical impacts of climate change wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Scientific opinion on climate change wikipedia , lookup
Public opinion on global warming wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and poverty wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on humans wikipedia , lookup
Surveys of scientists' views on climate change wikipedia , lookup
Climate change feedback wikipedia , lookup
Attribution of recent climate change wikipedia , lookup
IPCC Fourth Assessment Report wikipedia , lookup
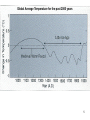
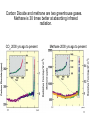
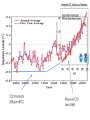
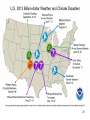
Climate Change Bause/Kulman North Farmington High School 1 Factors affecting climate • • • • • Atmosphere (the air) Hydrosphere (the water) Solid Earth (crust) Biosphere (life) Cryosphere (ice) *** A change in any one of these systems can cause a change in climate! 2 Is the Earth warming? Global average temperatures 18,000 yrs ago to present • YES!!! • For the past 20,000 years the Earth has been warming! • Which is why the glaciers are not here today. 3 From reconstructions of past climates, climate has varied… • • • from millions of years from thousands of years to even 100’s to 10’s of years. 4 Global Average Temperature for the past 2000 years 5 Land-based Surface Temperatures over the past 250 years 6 7 How do we know the climate has changed? • • Seafloor sediments – near surface organisms die and their remains become part of the sediments. – number/types of organisms change with changing climate Oxygen isotopes – measures the ratio of O16 to O18 found in ice and sedimentary rock. – O16 evaporates easier than O18. Because of this O16 is more often associated with precipitation. THUS becoming part of the glacial ice. – O18 is left in the water. So, during ice ages, there is more O18 in the water. And visa-versa – certain crustaceans use CaCO3 (called calcite) to make their shells. The Oxygen used is reflected in the shells. When the organism die, their hard shells become part of the ocean sediment. 8 Carbon Dioxide and methane are two greenhouse gases. Methane is 30 times better at absorbing infrared radiation. CO2 2000 yrs ago to present Methane 2000 yrs ago to present 9 10 Natural Causes of Climate Change (NOT caused by human activity) • • • • Plate Tectonics Volcanic Activity Sunspot Activity Milankovitch Cycles 11 Natural Cause of Climate ChangePlate Tectonics • Ice needs a land mass to collect on. • If there are no land masses along the poles, and thus more of them near the equator, typically these are times of warming. Currently there is no land mass directly on the North Pole, but close enough with Greenland. This allows ice to gather and stick around. 12 Natural Cause of Climate ChangeVolcanic Activity • volcanoes release of aerosols (tiny solids) increase atmospheric albedo and block insolation (incoming solar radiation). • Ex. 1815 Mt. Tambora “Year without a Summer”. Snow in June, frost in August. 13 Volcanoes or Humans? Mt. St. Helens Mt. Pinatubo Krakatoa Mt. Tambora The year without a summer Where’s Dante’s Peak? • The RED is a simple fit (or best fit) line. • The dips you see correspond to LARGE volcanic eruptions. • Despite the ash from the volcanic eruptions, the overall trend is increasing. 14 Natural Cause of Climate ChangeSunspot Activity • Sunspots are dark blemishes on the surface of the sun and are often associated with large solar eruptions. Sunspots Solar flare 50 times the diameter of Earth 15 Natural Cause of Climate ChangeSunspot Activity • Solar flares release LOTS of radiation. • Sunspots/flares are associated with an INCREASE in solar radiation reaching the Earth’s atmosphere which can warm the Earth 16 Natural Causes in Climate ChangeMilankovitch Cycles • Earth’s tilt changes on a 26,000 year cycle • Earth’s orbit becomes very elliptical, back to “circular” on a 100,000 year cycle. • Major glaciations occur when they both align. 17 Natural Causes in Climate ChangeMilankovitch Cycles • During circular orbits, Earth warms. • During elliptical orbits, Earth cools. 18 Human Impact of Climate ***Not just CO2*** • The FOUR “Fs” 1. Farming 2. Flatulence 3. Fertilizing 4. Fossil Fuels 19 Human Impact of Climate- Farming • Cutting down trees/vegetation for farming – Farm land/dark soil has less albedo than forests. • Stirring soil (tilling) releases naturally stored CO2 in soil aggregates. ***We’ve been doing this for 1000s of years*** 20 Human Impact of Climate- Flatulence • Methane (CH4) is produced from cattle, and from swamps (including artificial swamps used to grow rice). Also produced in landfills. • 20-30 times better at absorbing terrestrial radiation than CO2 21 Human Impact of ClimateFertilizing & Fossil Fuels • FERTILZING: Nitrous Oxide (N2O) is produced from nitrogen fertilizers • FOSSIL FUELS: CO2 AND N2O are produced during the combustion of fossil fuels. *** N2O is also a greenhouse gas and is 300 times better at absorbing infrared radiation than CO2*** 22 Consequences of Climate Change • The IPCC (Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change) states, "Taken as a whole, the range of published evidence indicates that the net damage costs of climate change are likely to be significant and to increase over time." 23 Consequences of Climate ChangeStorms Hurricane Sandy 2012 $65,000,000,000 2012 Midwest/Plains Drought $35,000,000,000 24 25 2014 Detroit Flood • Estimated cost of $1.1 billion 26 Consequences of Global WarmingStorm frequency 27 Water resources and agriculture • Changes in water distribution. SW US, a 2oC change in temp could result in 50% less precipitation. • Demands from the Colorado river now do not meet the needs. – it doesn’t even make it to the ocean anymore. 28 Consequences- Sea level rising • • As continental glaciers melt, water level will rise. It’s not just the glaciers melting! If temps go up, then the temps of oceans go up. If you increase heat, you increase the VOLUME (space) the water takes up. I hope Mickey knows how to SWIM!!! • Red indicates areas that will likely be under water. • NOTE: this is not the real Statue of liberty 29