* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Membrane Transport Notes
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
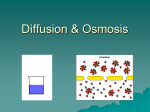
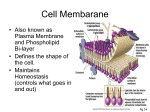
Cell Membrane Transport Notes Cell Membrane • Definition: The semi-permeable outercovering of all cells. • Composition: – 2 Phospholipid Layers – Protein Channels embedded • Purpose / Function: – Control traffic in and out of the cell – Protection Cell Wall • Definition: The rigid outer-covering of plant, and some bacterial cells. • Composition: – Cellulose (Plants) – Chitin (Fungi) – Peptidoglycan (Bacteria) • Purpose / Function: – Extra Support & Structure – Extra Protection Cell Membrane Transport • Methods: – Diffusion (No energy needed) – Osmosis (No energy needed) – Active Transport (Energy needed) • “Transport” = Things moving in and out of the cell. Concentration • Definition: The amount of matter in a given amount of space (area). • High Concentration = More matter in a given amount of space. • Low Concentration = Less matter in a given amount of space. • “Concentration Gradient”: A difference in concentrations. Permeability • Definition: The ability of matter to move across a boundary. • Cell Membranes are Semi-Permeable. • “Semi-Permeable”: The ability of only certain types of matter to move across a boundary. Fully Permeable Not Permeable Semi- Permeable Equilibrium • Definition: State of balance. • Matter moves in and out of cells to reach equilibrium. Diffusion • Definition: The movement of particles across a concentration gradient, from an area of higher concentration, to an area of lower concentration. Osmosis • Definition: The movement of water particles, across a concentration gradient, from an area of higher water concentration, to an area of lower water concentration. • *Water concentration with respect to Solute concentration! Solute & Solvent • Solute: Solid particles – Sugar – Salt • Solvent: Liquid which dissolves solute. – Water