* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Exploring Living Things
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
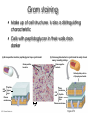
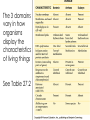
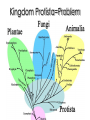
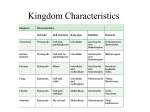
Lab Challenge: How will we determine the taxonomy of the microbes we find? Traditional Classification Chapter 26, 27 and 28 Understanding the 3 Domain; Kingdom System with a focus on Bacteria and Archaea Chapter References HEY!!! Let’s make this abundantly CLEAR--- when you see references to chapters, READ THEM! They are your HOMEWORK! Chapter 26 and 27 (selections) Reading Tips - Don’t read every word. Skim over all headings! Then, look for the parts of reading that match your notes Take NOTES by making a powerpoint! Unity: Characteristics of Living Things Made of Cells Respond to Stimuli Obtains materials Maintain and use energy Grow and Develop Reproduce Homeostasis Based on a Genetic Code Evolve Hierarchical Organization Binominal Nomenclature: 2 word naming system based on Genus species Did king philip come over for good soup? Shows relationships…what are they based on? Diversity: How can these characteristics show the diversity of living things? Focus on Bacteria All living things are MADE of CELLS, but size, shape, or arrangement may vary Focus on Bacteria Does the naming system make sense? Gram staining • Make up of cell structures is also a distinguishing characteristic • Cells with peptidoglycan in their walls stain darker (a) Gram-positive bacteria: peptidoglycan traps crystal violet. Gram-positive bacteria (b) Gram-negative bacteria: crystal violet is easily rinsed away, revealing red dye. Gram-negative bacteria Carbohydrate portion of lipopolysaccharide Cell wall Peptidoglycan layer Cell wall Plasma membrane 10 m Outer membrane Peptidoglycan layer Plasma membrane Figure 27.3 Response to environment Notetaking: what should you write down about this visual slide? Obtaining energy Nutrition is one important characteristic that allows us to compare. Into which group do you think our cheese microbe will fit? New characteristics force changes in classification What was the 2 kingdom model? The 5 kingdom model? How do the Domains and the current 6 kingdom model relate? What’s the current debate? Role of technology Using Molecular Data In 1977, Carl Woese used molecular data from ribosomal RNA to classify microbes. Previously, microbes classification was limited due to their lack of identifiable characteristics. http://dericbownds.net/uploaded_images/microbes2.gif Woese’s work led to the current three “domain” system of classification: Archaea, Bacteria, Eukarya http://aboundlessethic.com/wp-content/uploads/2007/10/treeoflife.gif 3 Domains The 3 domains vary in how organisms display the characteristics of living things See Table 27.2 What’s the difference between eubacteria and archaebacteria? Archaebacteria are more closely related to eukaryotes. Cell walls Eubacteria: Material-peptidoglycan Archaebacteria: Other materials Archaebacteria are usually extremophiles Halophiles Thermophiles How closely related are the kingdoms? Eukaryotes Key Characteristic= Nutrition If we use this as the basis, are fungi more closely related to animals or plants? Fungi: Heterotrophic decomposers Animals: Heterotrophic consumers Plants: Photoautotrophs Problems with using characteristics Maybe cell wall shows a better relationship. Does this agree with your previous hypothesis? Plants: Cellulose Fungi: Chitin (although some have no cell wall) Animals: No cell wall Chitin vs. Cellulose Note: Animals do not use chitin for a cell wall but can manufacture chitin for an exoskeleton…what do they need to make chitin? What do the genes tell us? General consensus: Fungi & Animals share most recent Common Ancestor. Jury is still out though… Active Reading Activity Read and take notes to answer a question…what information/vocab are important to that question! Section 28.1 Is the protista kingdom MONOPHYLETIC? (all share a common ancestor) Kingdom Protista=Problem Protists Are all protists closely related to eachother? Activity Take the information from your reading & notes and fill out the kingdom graphic organizer that you did in 9th grade! Discussion: Is this memorization? Direction… Later we will look at classification of the animal kingdom. As we go through the year, we will see the importance of understanding classification of plants, fungi, and protists.