* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Quizlet Voc Ch 18 19 Classification
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
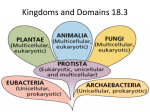
7 levels of classification (Largest to Smallest) kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, species Animalia kingdom of multicellular eukaryotic heterotrophs - cells do not have cell walls Archaebacteria kingdom of unicellular prokaryotes whose cell walls do not contain peptidoglycan; oldest bacteria, can live in extreme environments like volcanoes Bacteriophage Virus that attacks bacteria- made of a DNA core and a protein outer shell called a capsid binomial nomenclature a two-word naming system developed by Linnaeus (Genus species) Capsid Outer protein coat of a virus cladogram a diagram that shows the evolutionary relationships among a group of organisms - uses derived characters class group of similar orders derived character characteristics that appear in recent parts of a lineage but not in its older membersused to make a cladogram Eubacteria kingdom of unicellular prokaryotes whose cell walls are made up of peptidoglycan evolutionary classification the strategy of grouping organisms together based on their evolutionary history facultative anaerobe bacteria that can survive with or without oxygen family group of genera that share many characteristics Fungi kingdom composed of heterotrophs; many obtain energy and nutrients from dead organic matter, have cell walls made of chitin; once grouped with plants genus a group of closely related species; the capitalized part of an organism's scientific name Gram Staining Lab technique that identifies different types of bacteria based on differences in their cell walls kingdom largest taxonomic group, consisting of closely related phyla obligate aerobe bacteria requiring oxygen to survive obligated anaerobe bacteria that do not need oxygen to survive order group of similar families phylum group of closely related classes Plantae kingdom of multicellular photosynthetic autotrophs that have cell walls containing cellulose Protista kingdom composed of eukaryotes that are not classified as plants, animals, or fungi, have cell walls taxonomy the classification of organisms and assigning them a universally accepted name The eukaryotic kingdoms are... Protists, Plants, Fungi, Animals The prokaryotic kingdoms are... Eubacteria and Archaebacteria