* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Transformation Lab
Transcriptional regulation wikipedia , lookup
Gene regulatory network wikipedia , lookup
Promoter (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
Endogenous retrovirus wikipedia , lookup
Community fingerprinting wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Restriction enzyme wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
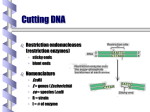
Transformation Lab What are plasmids? Circular sequences of DNA that can be incorporated into a bacterial host genome. What makes them so special?? They contain: -Origin of Replication -Selection Marker Gene (Amp) -Color Marker for easy selection pGREEN Plasmid Beta-galactosidase and X-gal • The beta-galactosidase gene encodes a protein that normally cleaves the disaccharide sugar lactose into galactose and glucose. However, the enzyme will also cleave many other molecules that contain structures resembling the galactoseglucose link. Researchers have developed several chemicals that, when cleaved by beta-galactosidase, produce colored products. One of these color indicators is the chemical 5-bromo-4-chloro3-indolyl-β-D- galactoside. Fortunately, the chemical is usually referred to by its common name, X-gal. X-gal is colorless, but when it is cleaved by beta-galactosidase, one of the products is dark blue. Therefore, if you grow bacteria that produce beta-galactosidase on media containing X-gal, the colonies will be bright blue. pBLU Plasmid Cloning • Cloning really means inserting DNA so that it is propagated in that cell and its progeny. • In order to do this in bacteria, the “gene of interest” has to be inserted into the plasmid (which is used as a vector). This is done in several steps. Restriction Enzymes •Restriction enzymes Cut DNA at specific sequences. •DNA Ligase reattaches that DNA into the plasmid