* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Cycle Control System - Santa Susana High School
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
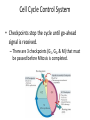
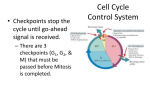
Cell Cycle Control System • Checkpoints stop the cycle until go-ahead signal is received. – There are 3 checkpoints (G1, G2, & M) that must be passed before Mitosis is completed. Molecules associated with the cellcycle clock • Cdks - cyclin-dependent kinase (remember that a kinase is an enzyme that activate or inactivate by phosphorylating) – cyclin is always present in the cell and is activated when phosphorylated – synthesized during the S-phase • MPF - M-phase promoting factor – – – – partner molecule to Cdk peaks during M phase and initiates Mitosis aids in the disassembly of the nuclear lamina switched off during Anaphase Molecules associated with the cellcycle clock • Growth factor – secreted by near-by cells – called a mitogen – many allow the cell to proceed past the G1 checkpoint • if the go-ahead signal is not reached it switches to the G0 phase – most adult cells are at this position External controls • density dependent inhibition – cells stop dividing when overcrowded • anchorage dependence – to divide cells must be anchored Cancer • Cancer cells lack the inhibition pathways – are immortal or stop at odd places in the cycle • HeLa cell line has been dividing since 1951 • usually 20-50 replications before cell death – normal cells are transformed to cancer cells through a transformation process – if the cells stay in the same location they are said to be benign – if the tumor invades an organ and impair its function, it is said to be malignant – when the cancer cells travel to different locations they are metastatic (process is metastasis)