* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Regulating the Cell Cycle - Milton
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
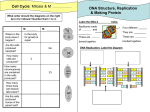
Regulating the Cell Cycle Learning Targets: “I can…” -Convert your percentages of cells in each phase into a pie chart to show how long the cell is in each phase. -Explain how each cell goes through a cycle with many checkpoints, and where mitosis fits within that cycle. -Name the four phases of the cell cycle and the important events of each. -Describe a factor outside of the cell that regulates the cell cycle. -Describe the role of p53. -Relate the cause of cancer to mitosis. A. What is the cell cycle? 1. The cell spends the majority of its life in ______________, when it is NOT ___________. 2. ___________ important phases occur during interphase of the cell cycle. During each phase, important events occur… a. G1 Phase: b. S Phase: c. G2 Phase: B. How is the cell cycle regulated? 1. The cell cycle contains ___________________ along the way before the cell proceeds into the next step. 2. These checkpoints can _______________ the cell from proceeding through the cell cycle if… a. ________________ are not lined up correctly b. ______ is damaged c. DNA is not ____________ C. What happens to cells when they are done dividing? 1. Newly divided cells are called ________ cells. 2. Before cells undergo _______________, they are stem cells. Stem cells have the potential (and can be forced) to become _______ type of cell. 3. Stem cells ____________ into ____________ types of cells. 4. Cells without _____________ can continue to ___________ indefinitely. 5. Cells can continue divide until they form a _______ of cells called a ____________. If the tumor affects surrounding cells, making them divide uncontrollably too, then _____________ has developed 6. Recent research has shown that a large number of cancer cells have a defect in the ________ _____, which normally _______ the cell cycle until all chromosomes have ____________.