* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Plant Biotechnology
Gene nomenclature wikipedia , lookup
RNA interference wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Genome editing wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Genetically modified food wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Genetically modified organism containment and escape wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
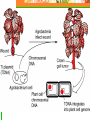
Plant Biotechnology Chapter 6 Fall 2008 CO2 + H2O →C6H12O6 + O2 Agriculture: The Next Revolution Biggest industry in the world ($1.3 trillion of products per year) Plant transgenesis allows innovations that are impossible to achieve with conventional hybridization methods (e.g. conventional -> strength of cotton 1.5%; insertion of a single gene > strength 60%!) Resistant to herbicides Pest resistant Vaccines 74% of all soybean crops are genetically modified 32% of all corn Methods Used in Plant Transgenesis Unique advantages of plants: The long history of plant breeding provides plant geneticists with a wealth of strains that can be exploited at the molecular level Plants produce large no.s of progeny; so rare mutations and recombinations can be found more easily Plants have been regenerative capabilities, even from one cell Species boundaries and sexual compatibility are no longer an issue Protoplast Fusion (figure 6.2) When injured, a mass of cells called a callus may grow over the site Callus cells have the capability to redifferentiate into shoots and roots Must remove the cellulose around these cells before DNA can be introduced; produce a protoplast Leaf Fragment Technique (figures 6.3 & 6.4) Small discs of leaf incubated with genetically modified Agrobacter Ti plasmid Treat with hormones to stimulate shoot and root development Limitation: cannot infect monocotyledonous plants only dicotyledonous such as tomatoes, potatoes, apples and soybeans Gene Guns Use on Agrobacter-resistant crops Blast tiny metal beads coated with DNA into an embryonic plant cell (figure 6.5) Aim at the nucleus or a chloroplast Shoot in gene of interest and a gene marker (reporter) Why is it more advantageous to genetically alter chloroplasts vs the nucleus? More genes can be inserted at one time, more likely to be expressed, DNA is separate from the nucleus (figure 6.6) Antisense Technology Flavr SavrTM tomato introduced in 1994 Ripe tomatoes normally produce the enzyme, polyglacturonase (PG) which digests pectin Scientists isolated gene, produced a complementary gene which produces a complementary mRNA that binds to the normal mRNA inactivating the normal mRNA for this enzyme (figure 6.7) RNA interference Inhibits gene expression by interfering with transcription or translation of RNA molecules http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/nova/sciencenow/3210/02.html Practical Applications in the Field (table 6.1) Vaccines for Plants (figure 6.8) Genetic Pesticides Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) Safe Storage (avidin-blocks the availability of biotin for insects) Herbicide Resistance –resistant to glyphosate (figure 6.10) Stronger fibers (already mentioned) Enhanced Nutrition Golden Rice (vit A) The Future: From Pharmaceuticals to Fuel Plant-based petroleum for fuels, alternatives to rubber, nicotine-free tobacco, etc Metabolic Engineering Manipulation of plant biochemistry to produce nonprotein products or to alter cellular properties Health and Environmental Concerns Human Health Allergens Environment Super weeds