* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download P57: Beckwith-Wiedemann Syndrome
Birth defect wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Oncogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Saethre–Chotzen syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Long non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of diabetes Type 2 wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Skewed X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
Mir-92 microRNA precursor family wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
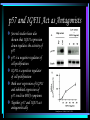
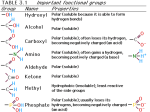
p57: Beckwith-Wiedemann Syndrome Presented By: Jameeka Carrington Symptoms of BWS Large body size (macrosomia) Large tongue (macroglossia) Large organs (visceromegaly) Abdominal wall defects (i.e. umbilical hernia ) Hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) Symptoms of BWS Large prominent eyes Creases in ear lobes Undescended testicles Seizures Symptoms of BWS Metopic Ridge- a ridge of bone or suture line on the forehead between the two halves of the frontal bone. The ridging is caused when the two halves close prematurely. www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/article/001186.htm Symptoms of BWS Microcephaly- abnormal smallness of the head Macroglossia- enlarged tongue Umbilical herniaprotrusion of the intestines through the abdominal wall in the navel region www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/article/001186.htm Symptoms of BWS Increased predisposition to tumor development Wilms’ tumor Adrenocortical carcinoma Rhabdomyosarcoma Hepatoblastoma Tests for BWS Bone X-ray Blood tests for low sugar Ultrasound of the abdomen X-ray of the abdomen MRI of the abdomen Chromosome studies Genetic Basis of BWS 85% of cases are sporadic Inherited in autosomal dominant fashion Mapped to chromosome 11p15 Translocation breakpoints found within chromosome map to three distinct regions Region 1, BWSCR1, contains 5 translocation breakpoints, which all disrupt the KCNQ1 gene and is the region of primary concern Chromosome 11 Steenman et al. (2000) Genes, Chromosomes & Cancer 28:2. p57 Member of the Cip/Kip family of mammalian CKI’s along with p21 and p27 Differs from p21 and p27 in structure by insert of proline/alanine rich or acidic motifs following the Cdk inhibitory domain Inhibits G1 cyclin-Cdk complexes by binding to cyclin and blocking the catalytic site of the associated Cdk Expressed during embryonic development The p21 Family of CDK inhibitors (p21CIP1/WAF1, p27KIP1, p57KIP2) active CDK Cyclin inactive + p21 CDK p21 Cyclin p27Kip1 Cyclin A CDK2 Jeffrey et al. (1995) Nature 376:313 CDK2 Cyclin A Russo et al. (1996) Nature 382:325 IGFII Insulin-like growth factor II, or IGFII, is a single chain polypeptide that is 47% homologous with insulin Functions Mediates growth hormone action Stimulates the growth of cultured cells Stimulates the action of insulin Involved in development and growth Autocrine regulator of cell proliferation Imprinting of p57 and IGFII p57 is paternally imprinted in the genome IGFII is maternally imprinted in the genome Genomic imprinting is the reversible modification of DNA that causes differential expression of maternally or paternally inherited genes A gene which is imprinted, is inactivated, by being methylated Imprinting suppresses gene transcription and takes place during gametogenesis Chromosome 11 is one of only nine chromosomes that are suspected to have imprinted regions p57 and IGFII Act as Antagonists Several studies have also shown that IGFII expression down regulates the activity of p57 p57 is a negative regulator of cell proliferation IGFII is a positive regulator of cell proliferation Both over expression of IGFII and inhibited expression of p57 result in BWS symptoms Together, p57 and IGFII act antagonistically Grandjean et al. (2000) PNAS 97:5281. Loss of Imprinting (LOI) and BWS Imprinting defects of IGFII is the most prominent cause of the development of BWS LOI of IGFII results in biallelic expression of IGFII, which down regulates expression of p57 at an increased level Paternal duplication of IGFII and the presence of a defective maternal p57 allele contributes to the development of BWS as well Weksburg et al. (2001) Human Molecular Genetics 10:2989-3000. p57 and BWS Two separate studies were conducted using mutant mice carrying deletions of the beginning of the p57 gene Resultant defects common between both studies correlate with symptoms of BWS Phenotype BWS p57KIP2 mutants IGFII transgenics Macroglossia + _ nd Gigantism + _ +* Abdominal defect + + nd Hypoglycemia + _ + Visceromegaly + + + Renal dysplasia +/- + nd Adrenal cytomegaly + + nd Intestinal malrotation +/- + nd Cleft palate +/- + nd Neoplasia +/- _ +* Skeletal anomalies +/- + nd Lens defect +/- + nd Key: +, observed commonly; +/-, less commonly observed; -, not observed; nd, not determined; *, observed only in some reports Swanger, W. Jherek, Roberts, James M. (1997) BioEssays 19:840. Summary BWS is an autosomal dominant disorder characterized by overgrowth and predisposition to tumor development p57 and IGFII, both located on chromosome 11, are believed to be highly associated with the development of BWS Defects in the imprinting of p57 and IGFII have been experimentally shown to reproduce BWS symptoms in mutant mice