* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Mendel & Genes
Inbreeding avoidance wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Human–animal hybrid wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance wikipedia , lookup
Human leukocyte antigen wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
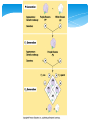
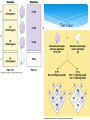
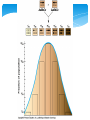
Mendel & the Gene Idea Gregor Mendel – Pea-rific! Bred garden peas in monastery Character – heritable feature Trait – variant for a character Cross-pollinated true-breeding varieties of pea plant (hybridization) “Parents” – P generation Offspring – F1 generation F1 offspring – F2 generation Mendel’s Work P: purple & white F1: all purple F2: 75% purple 25% white How? Hypothesis… Mendel’s Work 1. 2. Alternative versions of genes (alleles) account for variations in inherited characteristics For each character, you inherit one allele from each parent Mendel’s Work 3. If the two alleles differ… Dominant allele - fully expressed Recessive allele – no noticeable effect on appearance Mendel’s Work 4. Two alleles segregate (separate) during gamete production Each gamete gets one This is the Law of Segregation Determined by Punnett square Vocabulary to know Homozygous – have two of same allele Heterozygous – two different alleles Phenotype – physical appearance & physiological makeup Genotype – genetic makeup Testcross – test unknown with homozygous recessive to determine unknown genotype Test Cross Law of Independent Assortment Each different pair of alleles will segregate independent of any others during gamete formation F1 produced for single character – monohybrid F1 produced for two characters – dihybrid Result of dihybrid cross - 9:3:3:1 Math Rules Rule of Multiplication Probability two independent events happen at same time – multiply each probability Coin: H & H = ½ x ½ = ¼ F1 is Pp – chance F2 is pp? Gamete has P = ½ Gamete has p = ½ ½ x ½ = ¼ Math Rules Dihybrid crosses YyRr x YyRr Probability of YYRR Do a Punnett square for Yy x Yy Get ¼ Do another for Rr x Rr Get ¼ ¼ x ¼ = YY AND RR = 1/16 Math Rules Rule of Addition Probability of event that can occur two or more different ways – add sum of separate probabilities Example: cross two Heterozygous for flower color probability that the offspring is heterozygous? 1)Mom’s recessive egg with dad’s dominant sperm – ¼ 2)Dad’s recessive sperm with mom’s dominant egg – ¼ #1 OR #2 ¼ + ¼ = ½ Mendel & Beyond Incomplete Dominance F1 hybrids have intermediate characteristics Ex: snapdragons Not blending Mendel & Beyond Codominance Two alleles in hybrid are BOTH expressed Ex: blood types Mendel & Beyond Multiple Alleles Blood type A, B, AB, O Three alleles – Ia, Ib, i Presence or absence of carbo on surface Wrong blood type – agglutination Mendel & Beyond Quantitative characters Characters that vary along a continuum Ex: human skin color Indicates polygenic inheritance Additive effect of two or more genes on single phenotypic character Nature vs Nurture Both often have an effect on gene expression Human Inheritance Chart with a pedigree Human Inheritance Recessively Inherited Disorders Need homozygous recessive to have Heterozygous are carriers & can pass on to offspring Ex: Cystic fibrosis, Tay-Sachs, sickle-cell disease Read details in text Human Inheritance Dominantly Inherited Disorders Achondroplasia (dwarfism), cluster headaches Affects homozygous dominant & heterozygous If lethal, much less common – die before reproducing Human Inheritance If late-acting, can pass on dominant disorder Ex: Huntington’s disease Multifactorial Disorders Genetics & environment play a role Ex: diabetes, cancer, some mental illness Technology Fetal Testing Amniocentesis Chorionic villis sampling (CVS) Ultrasound