* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 14.1 Test Cross and Law of independent assortment
Survey
Document related concepts
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Human leukocyte antigen wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
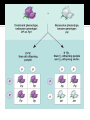
By: Savannah Rodamer Alleles- alternative versions of a gene Dominant Allele- determines the organisms appearance Recessive Allele- has no noticeable effect on the organisms appearance Law of segregation- two alleles for a heritable character segregate during gamete formation and end up in different gametes Punnett square- diagrammatic device for predicting the allele composition of offspring from a cross between individuals of known genetic makeup Homozygous- Organism that has a pair of identical alleles Heterozygous- Organism that has two different alleles for a gene Phenotype- Organisms appearance/physical traits Genotype- Organisms genetic makeup Monohybrids- individuals heterozygous for one character Dihybrids- individuals heterozygous for two characters (YyRr) Law of Independent assortment- each pair alleles segregates independently of each other pair of alleles during gamete function Test Crossing was first introduced by Gregor Mendel It is used to determine if a group that has a dominant trait is homozygous or heterozygous for that particular trait Test crosses determine the genotype of an individual with a dominant phenotype The genotype of an offspring is determined by the allele inherited from its parents There is a monohybrid cross and a dihybrid cross Basic principle of genetics and occurs in meiosis Alleles for different traits separate when gametes are formed without influencing inheritance At fertilization, the alleles randomly unite Mendel first used pea plants to show the law of independent assortment. Using a green pod that produced yellow seeds and a yellow pod that produced green seeds to represent a dihybrid cross If a tall tomato plant has the dominant allele T and a dwarf tomato plant has the recessive allele t. Create a punnet square. T t T TT Tt t Tt tt What is a test cross used for? A:To determine an individuals genotype During gamete formation genes for different traits separate without influencing each other’s inheritance. This illustrates which Law? A: Law of Independent Assortment http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Y1PCwxU DTl8 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Test_cross http://lifesci.rutgers.edu/~mcguire/toolboxdemo/Testcross/test_cross.htm http://biology.about.com/od/mendeliangenet ics/ss/independent-assortment.htm http://biology.about.com/library/glossary/bld efmenlawia.htm