* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CoDominance Worksheet
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
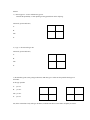
Name______________________ PER__________ Date__________ This worksheet gives you practice in problems dealing with incomplete dominance. Below is a complete example for you to follow. Important information: Codominant traits are different from simple dominant traits because heterozygous individuals can have multiple dominant alleles. This results in both traits being expressed simultaneously. There is also a recessive trait that can be present. EXAMPLE: Blood type: Type A: IAIA or heterozygous A: IAi Type B: IBIB or heterozygous B: IBi Type AB: IAIB Type O: ii Note: IA denotes that the allele is a dominant allele form "A". The "A" protein will be made on the red blood cells. IB denotes that the allele is a dominant allele form "B". The "B" protein will be made on the red blood cells IA IB denotes that the individual has both forms of dominant alleles "A" and "B". Both proteins made. ii denotes that the individual has both recessive alleles. No proteins made on red blood cell. Parent A: Heterozygous A Parent B: Homozygous B Calculate the probability of each phenotype being passed down to the offspring. INFORMATION: I A i I B IAIB IB i I B IAIB IB i Notice how the punnett square is set up so that one parent has the genotype across the top. The other parent's genotype is down the side. The table is filled in according to the corresponding genotype. TOTALS: A: 0 out of 4…….0/4 B: 2 out of 4……..2/4 AB: 2 out of 4……2/4 O: 0 out of 4…….0/4 If the question asks for a ratio, you must do the following: -Use the total for that phenotype. -Write the ratio with a labeled number. Ratio for above problem: 0: 2:2:0 Ratio for above problem: 0A: 2B : 2AB : 0 O Practice: 1.) Heterozygous A crosses with Heterozygous A. Calculate the probability of each phenotype being passed down to the offspring. TOTALS: (percent and ratio) A: B: AB: O: 2.) Type O breeds with Type AB TOTALS: (percent and ratio) A: B: AB: O: 3.) Woman has type B (exact genotype unknown). Man has type O. What are the possible blood types of their kids? Is this type possible: A: yes/ no? B: yes/ no? AB: yes/ no? O: yes/ no? 3B.) If the woman has a baby with type AB blood, could the man above be the father? Explain you answer.