* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 12.3 and12.4 notes CD
Epigenetics of diabetes Type 2 wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Fetal origins hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Pathogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Gene nomenclature wikipedia , lookup
Gene desert wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
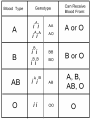
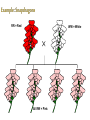
A Punnett square shows the possible outcomes of a cross, but it can also be used to calculate the probability of each outcome. Probability is the likelihood that a specific event will occur. Probability can be expressed in words, as a decimal, as a percentage, or as a fraction. Probability formulas can be used to predict the probabilities that specific alleles will be passed on to offspring. The possible results of a heterozygous cross are similar to those of flipping two coins at once. A pedigree is a diagram that shows how a trait is inherited over several generations of a family. Pedigrees can be used to help a family understand a genetic disorder. A genetic disorder is a disease or disorder that can be inherited. A pedigree can help answer questions about three aspects of inheritance: sex linkage, dominance, and heterozygosity. Human generations are longer than 20 years Must rely on family histories and medical records Pedigree diagram that follows the inheritance of a single gene through several generations in a family = Male, O = Female connects parents connects parents to children children are placed from left to right in birth order Homozygous trait shaded in Heterozygous trait 1/2 shaded Are there exceptions to the simple Mendelian pattern of inheritance? How do heredity and the environment interact to influence phenotype? How do linked genes affect chromosome assortment and crossover during meiosis? Most patterns of inheritance are more complex than those that Mendel identified. The Mendelian inheritance pattern is rare in nature; other patterns include: polygenic inheritance incomplete dominance multiple alleles codominance. Polygenic character A character that is influenced or affected by more than one gene Examples: Eye color, height, and skin color Most characters are polygenic. Multiple alleles Genes that have three or more possible alleles Example: control the ABO blood groups (blood types) in humans. Incomplete Dominance A condition where an offspring has a phenotype that is intermediate between the two traits of its parents Example: Snapdragons: red and white with the intermediate trait being pink R- gene for red flowers, W- gene for white flowers: RR- red, WW- white, RW- pink RR = Red WW = White All RW = Pink Codominance a condition in which both alleles for the same gene are fully expressed. Example: The genetics of human blood groups Another example- Chicken feathers B- gene for black feathers, W- gene for white feathers: BB- black, WW- white, BW- “erminette” Black and White! Phenotype can be affected by conditions in the environment, such as nutrients and temperature. In humans, many characters that are partly determined by heredity, such as height, are also affected by the environment. Many aspects of human personality and behavior are strongly affected by the environment, but genes also play an important role. The Mendelian inheritance pattern is rare in nature; other patterns include polygenic inheritance, incomplete dominance, multiple alleles, and codominance. Phenotype can be affected by conditions in the environment, such as nutrients and temperature. During meiosis, genes that are close together on the same chromosome are less likely to be separated than genes that are far apart.