* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Barbara McClintock
Gene nomenclature wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Gene desert wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Saethre–Chotzen syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Transposable element wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Skewed X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
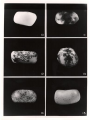
Barbara McClintock By Kalim Kassim and Tim Milsom Prior Knowledge In 1938, Marcus Rhodes provided the first description of an unstable mutation, found by using maize. This resulted in a variegated phenotype which produces irregular patterns of pigmentation and pigment production. 2 genes caused this irregularity: the unstable allele by one gene and a dominant mutation by the second gene called Dotted. Barbara Mclintock In the 1940’s and 1950’s, she showed that this irregularity was caused by genetic elements that moved or transposed from one locus to another. She studied the mosaic patterns of maize seeds and the inheritance of these patterns. She found 2 new dominant genetic loci that she names Dissociatior (Ds) and Activator (Ac) Dissociator caused the chromosomes to break and effected neighbouring genes when the activator was present. Later, in 1948, she found that Ds and Ac could transpose on the chromosome. By changing the colouration of the kernels over each generation, by using controlled crosses, she concluded that Ac controls the transposition of Ds from chromosome 9 and when Ds is moved there is a breakage in the chromosome. Conclusion When Ds moves, the color gene is released which causes colour Mosaicism is caused by Ds transposing in random cells and not every cell. Size of the spot is determined by seed development Transposition of Ds is determined by the number of Ac copies Ac controls the transposition of Ds from chromosome 9 and when Ds is moved there is a breakage in the chromosome. Works Cited http://mcb.berkeley.edu/courses/mcb140/garri ga_08/McClintock_notes.pdf Accessed December - 20 – 11 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Barbara_McClinto ck Accessed December - 20 – 11