* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Inheritance - World of Teaching
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Genome editing wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
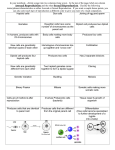
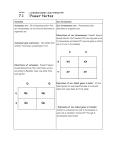
Genetics and inheritance Aim: 1. To recall the important terms that relate to genetics and inheritance (KS4) 2. Describe the basic structure of DNA In your own words, explain the following terms 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. Chromosome Gene Features Gametes Zygote Diploid Allele Homozygous Heterozygous Selective breeding Genetic engineering Meiosis Mitosis Sexual reproduction Asexual reproduction Mutations Dominant Recessive These are the units which make up chromosomes. Responsible for inheritance of specific characteristics These are things like eye colour, skin colour and hair colour. They are controlled by genes. Sperm and egg cells are both this type of cell. Contain half the amount of DNA of normal diploid cells When a sperm and egg cell fuse together, they produce this. We use this word to describe cells which contain the full complement of genetic material. In humans this would be 46 chromosomes (23 pairs) The different versions of genes Alleles of a given gene are not identical Where plants and animals with useful or desired traits are bred together to produce offspring with those desired traits The altering of the character of an organism by inserting genes from another organism Division of a cell to produce 2 daughter cells which each has the same number and kind of chromosomes as the mother cell Type of reproduction that involves fusion of gametes Random change in the genetic material of the cell The allele that is expressed where an individual is heterozygous The allele that is ‘hidden’ (not expressed) when an individual is heterozygous for a given gene What does it look like? This powerpoint was kindly donated to www.worldofteaching.com http://www.worldofteaching.com is home to over a thousand powerpoints submitted by teachers. This is a completely free site and requires no registration. Please visit and I hope it will help in your teaching.