* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Basis of Heredity
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Hybrid (biology) wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Life history theory wikipedia , lookup
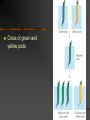
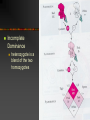
The Basis of Heredity Inheritance and Meiosis Definitions Genetics = study of genes, the units on chromosomes that code for traits Heredity = study of how traits are passed on The Inheritance of Traits: Mendel’s Discoveries Czechoslovakian monk First to discover rules of inheritance Published work in 1865 Mendel’s Hybrid Peas Pure lines: tall plants made tall plants Studied 7 contrasting characteristics Mendel’s Crosses Mendel looked at one trait at a time by crossing inbred lines. Hybrid = offspring produced by breeding two pure lines. P1 = purebred parents. F1 = first generation of offspring. F2 = second generation of offspring. P = parental F = filial or offspring. Cross of green and yellow pods Mendel Crossed Short X Tall P1 tall x short F1 all tall F2 3/4 tall 1/4 short. hypothesis: 2 factors controlling height. Factor for shortness was hidden in F1. (expected medium) Short X Tall Continued Tall factor = dominant (masked short) Short factor = recessive (was hidden) Mendel tested his hypothesis - crossed plants with other 6 traits All other traits acted in same way The Law of Segregation Mendel noticed 2 things Explained results with Law of Segregation factors controlling traits were distinct units traits appeared in constant proportions in F2 individual carries 2 factors for each trait each parent contributes 1 of the 2 factors TT and Tt = tall and tt = short genes = units of heredity Alleles = 2 separate forms of a gene Genotype Vs. Phenotype Genotype = the alleles of an organism Phenotype = the appearance of an organism Homozygous = having 2 identical alleles TT or tt Heterozygous = having unlike alleles - Tt Using Punnett Squares Test Cross Used to determine if an individual is homozygous or heterozygous Incomplete Dominance heterozygote is a blend of the two homozygotes Law of Independent Assortment monohybrid cross: involves one pair of alleles or one gene dihybrid cross: crosses involving two genes Mendel did thousands of dihybrid crosses which led to law of independent assortment the inheritance of one gene does not affect the inheritance of another gene a tall plant can have either smooth or wrinkled seeds Meiosis The Cellular Basis of Heredity Chromosome Number somatic cells = body cells diploid = 2 sets of chromosomes - 2n n = # of different kinds of chromosomes haploid = 1 set of chromosomes most organisms contain two complete sets of chromosomes humans n = 23(haploid) and 2n = 46(diploid) homologous chromosomes = matching pairs Asexual and Sexual Reproduction Asexual reproduction offspring genetically identical to parent offspring formed by mitosis potato production Sexual reproduction 2 haploid cells unite to form a diploid cell haploid cells = gametes (sperm and eggs) fertilization = union of two gametes to form zygote zygote grows by mitosis to form new organism