* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download cross-fertilized
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Genetically modified crops wikipedia , lookup
Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Hybrid (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
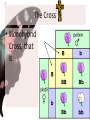
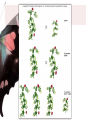
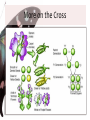
Mendel’s Genetics Chapter 11 Who was Gregor Mendel? – He was known as the “FATHER OF GENETICS” – He discovered how traits were inherited • GENETICS – study of heredity • HEREDITY – the passing of traits from parents to offspring Mendel’s Peas – Mendel did his study on pea plants – Pea plants have many traits (tall/short, purple flowers/white flowers) – Pea plants can be self-fertilized or cross-fertilized True Breeding • Meaning that if they are allowed to selfpollinate, they will produce offspring identical to themselves – Self-pollinate: some plants have both male and female flowers – One plant is producing both male and female gametes that are fertilized Dominance • Some traits are dominant over others. • Tall x Short = all tall offspring (hybrids) • *Tall is the dominant trait • * Short is recessive Genes and Alleles • Mendel discovered that each trait is controlled by two factors (alleles) • Genes – factors that determine your traits Mendel’s Experiments The Cross • Monohybrid Cross, that is Explaining the Cross • When a parent makes sperm or eggs, their genes separate (PRINCIPLE/LAW OF SEGREGATION) • The GAMETES (egg or sperm) contain either a T allele (tall) or a t allele (short) – This works for various traits like hair color More on the Cross Genes→Traits • GENOTYPE - what genes ( letters) the organism has (TT, Tt, tt) • PHENOTYPE - what it looks like (tall or short) Understanding Check 1. A one-eyed purple people eater is crossed with a two eyed purple people eater. All of their offspring have two eyes. Which trait is dominant? • 2. If you use the letter E for this gene. What is the genotype of the offspring? • Are these offspring the F1 or F2 generation? • 4. If you crossed the offspring with each other? How many ofthe new offspring would you expect to have two eyes? Incomplete Dominance • When both alleles are expressed, making colors somewhere in the middle – More like a mixing of the two alleles Codominance • When both alleles are expressed equally – Not mixing, but blotched usually Another Cross • Dihybrid Cross – When you do a cross for two traits at the same time – For example: a cross for eye AND hair color Example Cross • What do you get when you cross a tall purple flower plant with a short white flower plant???