* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Folate Production and Lysis
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
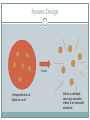
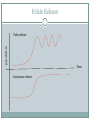
Folate Production and Lysis VICTORIA System Design Lysis Overproduction of folate in e coli Folate is released into large intestine where it is eventually absorbed Folate Production folE Biosynthetic pathway of folate folB folK folP folB folA DHFR Bermingham et al. 6 enzymatic steps + final reduction step GTPCH1 - GTP Cyclohydrolase I (folE) DHPP -7,8-Dihydroneopterin triphosphate pyrophosphohydrolase DHNA - 7,8-Dihydroneopterin aldolase (folB) HPPK - 6-Hydroxymethyl-7,8-dihydropterin pyrophosphokinase (folK) DHPS - Dihydropteroate synthase (folP) FPGS - Folylpoly-g-glutamate synthetase (folC) DHFR – dihydrofolate reductase (folA) Reduces 7,8-dihydrofolate 5,6,7,8-tetrahydrofolate PABA & glutamate For B.Subtilis – pabA, pabB, pabC were used to make PABA from chorismate Zhu et al L.Lactis folate gene cluster Sybesma et al Controlled Lysis •Prophage •the T4 holin + the T7 lysozyme •the ldcA deletion Folate Release population Pulse release Time Continuous release pLysT – T4 gene t (Morita) •Produces T7 lysozyme which degrades petidoglycan, but won’t lyse the cell until the expression of T4 holin (expressed by gene t) which creates a break in the membrane, allowing the T7 to reach the peptidoglycan layer. •Requires IPTG to trigger expression of the plasmid. Morita et al. Programmed Escherichia coli Cell Lysis by Expression of Cloned T4 Phage Lysis Genes. Biotechnol. Prog. 2001, 17, 573-576 ldcA deletion ldcA encodes a cytoplasmic L,D-carboxypeptidase which creates peptide bonds in the peptidoglycan layer between the inner and outer membranes. Normally, the murein (peptidoglycan) is continuously recycled into a pentapeptide and replaced. Deleting ldcA results in the accumulation of a tetrapeptide instead of a pentapeptide, causing a weakened cell wall, and resulting in spontaenous autolysis during the stationary growth phase. Can the E.coli reach a stationary growth phase in the intestine? The E.coli would become more and more fragile as time goes on since it’s still recycling the good murein but not replacing it, so eventually it would lyse? Templin et al. A defect in cell wall recycling triggers autolysis during the stationary growth phase of Escherichia coli. The EMBO Journal Vol.18 No.15 pp.4108–4117, 1999