* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Epigenet-web
Whole genome sequencing wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Community fingerprinting wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Secreted frizzled-related protein 1 wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
Promoter (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Endogenous retrovirus wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Transcriptional regulation wikipedia , lookup
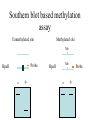
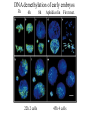
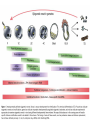
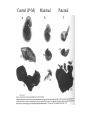
All the cells in the organism have the same DNA • DNA is packed together with histones and other proteins into chromatin. • Chromatin is a highly dynamic material which carries a substantial amount of epigentic information. • All cells in the organism carry the same genetic material, however each cell type expresses different genes. Epigenetics • Epigenetics - Heritable changes in gene expression that operate outside of changes in DNA itself Chromatin remodeling • Protein expression can be induced and repressed over many orders of magnitude. An important part of this regulation is exerted via chromatin remodeling by DNA methylation and numerous modifications mainly of the N-termini of histones - acetylation, methylation, phosphorylation and ubiquitilation. There might be up to about 150 different such modifications !!!! Epigenetic chromatin regulation A. Modification at the DNA level cytosine methylation The five nucleotides that make up the DNA CpG dinocleotides are palindromic 5’ CpG 3’ 3’ GpC 5’ CpG dinocleotides are palindromic 5’ CpG 3’ 3’ GpC 5’ To be recognized as a CpG island, a sequence must satisfy the following critera: 1. (G+C) content of 0.50 or greater 2. an observed to expected CpG dinucleotide ratio of 0.60 or greater 3. and both occurring within a sequence window of 200 bp or greater. CpGs are vastly underrepresented genome-wide compared to what would be expected by chance (0.23 in the human genome and 0.19 in the mouse genome, respectively) This is because deamination of cytosine gives rise to uracil, which is easily recognized as foreign within the DNA strand and replaced, whereas deamination of methylcytosine gives rise to thymine, which is less readily recognized as foreign and therefore prone to mutation and depletion in the genome. CpG island definition based on sequence composition identifies these elements at the promoter sites of approximately half of the genes in the human genome, most of which are expressed in most or all tissues, hence their designation as ‘housekeeping’ genes. Mutations at 5’ methyl cytosine cannot be identified and repaired Maintenance of methylation DNMT1 Brand eis, M., Ariel, M. & Cedar, H. ( 1 99 3 ) Bioessays 1 5 , 70 9-71 3. Southern blot based methylation assay Unmethylated site Methylated site Me Probe HpaII - + Me HpaII - Probe + Methylation is globally erased during gametogenesis and embryogenesis Kafri, T., Ariel, M., Brand eis, M., Sh emer, R., U rven, L., McCarrey, J., Cedar, H. & Razi n, A. (199 2) Genes Dev 6, 705-714. DNA demethylation of early embryos 3h 6h 8h Aphidicolin First met. P P P M M M P M 22h 2 cells Mayer, W., N iveleau, A., W alt er, J., Fund ele, R. & Haaf , T. ( 20 00) Natu re 40 3, 501-2 45h 4 cells Establishment of DNA methylation pattern • The methylation pattern of the genome is established anew every generation. In that sense methylation is an epigentic phenomenon - it influences the genetic material but it is not inherited from one generation to another. • All methylation (or at least almost all) is erased during early embryogenesis and reestablished DNMT3 Roles of DNA methylation • • • • • Transcriptional silencing Protecting the genome from transposition Genomic imprinting X inactivation Tissue specific gene expression Histone code or language ? Role of histone acetylation • Acetylated histones open up the chromatin and enable transcription. Histones are acetylated by HAT (histone acetylases) which are parts of many chromatin remodeling and transcription complexes. Role of histone de-acetylation • Deacetylated histones are tightly packed and less accessible to transcription factors. • Histones are deacetylated by HDAC (histone de-acetylase) proteins. Epigenetic chromatin regulation A. Modification at the DNA level 1. cytosine methylation B. Histone modification - the histone code 1. Histone acetylation 2. Histone methylation 3. Histone phosphorylation 4. Histone ubiquitilation 5. Different types of histones Mono-allelic expression Smell Immune system X chromosome Genomic imprinting Some genes are expressed only from the maternal genome and some only from the paternal genome It is estimated that about 80 genes are imprinted and they can be found on several different chromosomes For example - igf2, h19, igf2r and genes involved in the Angelman and Prader Willi syndromes Control (P+M) Maternal Paternal Imprinting is maintained by DNA methylation Obligatory reading: Lande-Diner, L. & Cedar, H. Silence of the genes-mechanisms of long-term repression. Nat Rev Genet 6, 648-54 (2005). Griffiths chapter 12 - genomics