* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Per cent of children with 1st cousin parents
DNA paternity testing wikipedia , lookup
Gene nomenclature wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of diabetes Type 2 wikipedia , lookup
Genetic testing wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Cancer epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Genealogical DNA test wikipedia , lookup
Oncogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Genome editing wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
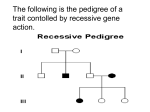
DNA Analysis electrophoresis: separation of molecules in an electric field DNA moves toward the positive electrode in an electric field due to the huge number of phosphate groups in the DNA backbone DNA fragments migrate through the gel proportional to their size small pieces quickly, large pieces slowly for agarose gels, bands are usually visualized with ethidium bromide the percentage of agarose determines what size DNA is separated well DNA Analysis normal agarose gels separate tens to thousands of base pairs pulsed field gels can separate thousands to 106 base pair range by regularly changing the direction of the electric field net direction is always toward + end acrylamide gels separate DNA down to the level of a single base 0 Great Britain SW Peninsula Dorset & Somerset Chesh & Mersey N & E Yorks & N Lincs Kent & Medway Essex Hamps & IoW Avon Glouc & Wilts Wales Norfk, Suffk & Cambs Surrey & Sussex SE London Nthumber Tyne & Wear Leics N'thants & Rutld Durham & Tees Vall Cov War Heref & Worcs Trent Shropsh & Staffs N Centr London SW London S Yorkshire Bedfdsh & Herts Thames Valley Cumbria & Lancs NW London Gter Manchester NE London B'ham & Bl Country W Yorkshire % of children Per cent of children with 1st cousin parents 7 6 5 4 Ethnic minority 1C parents 3 2 N Euro 1C parents 1 Sex Chromosomes Fig. 11.14b Pedigree showing the transmission of the X-linked dominant trait of faulty tooth enamel Peter J. Russell, iGenetics: Copyright © Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings. Sex-linked Disorders • A male only receives such sex-linked alleles from his mother. (The homologous Y chromosome is always inherited from the father.) • A male therefore needs only one copy of a sexlinked recessive allele to exhibit the recessive trait. • In contrast, a female must inherit two such recessive alleles—one from each parent—to exhibit the trait Gene variants all follow the same inheritance pattern (some exceptions) Partner who carries a gene variant Not a carrier Partner who does not carry the variant Carrier of the gene variant Not a carrier Carrier of the gene variant Gene variants all follow the same inheritance pattern (some exceptions) Partner who carries the same gene variant Partner who carries a gene variant Not a carrier Carrier of the gene variant Carrier of the gene variant Person homozygous for the gene variant Types & Size of GCRC Studies • Familiy studies (linkage, sib pair &TDT) TDT Linkage Sib pair • Association studies • Drug metabolizing gene studies ddA Trace A/A A/G G/ G Genetic diagnosis DNA protein metabolite Blood gp ABO, Rh G6PD deficiency Hb variant Apo E 1-4 bilirubin phenylalanine cholesterol homocysteine Genetic diagnosis DNA haemochromatosis MTHFR cystic fibrosis familial hypercholesterolaemia (FH) protein metabolite Blood gp ABO, Rh G6PD deficiency Hb variant Apo E 1-4 bilirubin phenylalanine cholesterol homocysteine Extended family Nuclear family Specialist - Affected person clinical geneticist paediatrician, cardiologist A known diagnosis: the aim of family studies is to identify relatives with, or without, a specific variant Extended family Nuclear family GP, with any patient A genetic family history can identify risk by locating relatives with relevant disorders Family history: a pincer movement on families Extended family Nuclear family Specialist clinical geneticist paediatrician, cardiologist A known diagnosis: the aim of family studies is to identify relatives with, or without, a specific variant GP, with any patient A genetic family history can identify risk by locating relatives with relevant disorders Different approaches from specialist and PHC perspectives A CF Spec ialist B C Primary care D Ca bowel 48 59 67 D cot death D accident D blood clot 91 72 49 57 Ca cervix 43 Ca bowel 42 CoD not noted 46 43 44 41 43 Int polyp removed 40 18 15 4 D Ca bowel 48 59 67 D cot death D accident D blood clot 91 72 49 57 Ca cervix 43 Ca bowel 42 CoD not noted 46 43 44 41 43 Int polyp removed 40 18 15 4 D Ca bowel 48 59 67 D cot death D accident D blood clot 91 72 49 57 Ca cervix 43 Ca bowel 42 CoD not noted 46 43 44 41 43 Int polyp removed 40 18 15 4 D stroke 60 D stroke 61 hypertension D Ca ovary 50 D Ca ovary 48 Manic depressive D stroke 60 D stroke 61 hypertension D Ca ovary 50 D Ca ovary 48 Manic depressive D stroke 60 D stroke 61 hypertension D Ca ovary 50 D Ca ovary 48 Manic depressive D stroke 60 D stroke 61 hypertension D Ca ovary 50 D Ca ovary 48 Manic depressive 77 74 73 D heart attack 55 D emphysema 77 D heart attack 71 ? No. 54 ? No. 51 41 36 56 51 53 Epilepsy Asthma Asthma Alzheimer's 50 ? No. 27 25 18 Asthma 1 Asthma 1 Hay fever Asthma/ eczema 1 Food allergies to 11yr 77 74 73 D heart attack 55 D emphysema 77 D heart attack 71 ? No. 54 ? No. 51 41 36 56 51 53 Epilepsy Asthma Asthma Alzheimer's 50 ? No. 27 25 18 Asthma 1 Asthma 1 Hay fever Asthma/ eczema 1 Food allergies to 11yr 77 74 73 D heart attack 55 D emphysema 77 D heart attack 71 ? No. 54 ? No. 51 41 36 56 51 53 Epilepsy Asthma Asthma Alzheimer's 50 ? No. 27 25 18 Asthma 1 Asthma 1 Hay fever Asthma/ eczema 1 Food allergies to 11yr 77 74 73 D heart attack 55 D emphysema 77 D heart attack 71 ? No. 54 ? No. 51 41 36 56 51 53 Epilepsy Asthma Asthma Alzheimer's 50 ? No. 27 25 18 Asthma 1 Asthma 1 Hay fever Asthma/ eczema 1 Food allergies to 11yr old age 80 old age 80 Committed Committed suicide 20 suicide 20 Cancer 70 88 Heart attack 60 Old age 80 Arrythmia 85 69 Committed suicide 25 Arrythmia 68 38 Thalassemia carrier 64 Thalassemia carrier Hysterectomy 40 40 endometriosis Old age 70 Cancer 60 old age 80 old age 80 Committed Committed suicide 20 suicide 20 Cancer 70 88 Heart attack 60 Old age 80 Arrythmia 85 69 Committed Arrythmia 68 suicide 25 38 Thalassemia carrier 64 Thalassemia carrier Hysterectomy 40 40 endometriosis Old age 70 Cancer 60 old age 80 old age 80 Committed Committed suicide 20 suicide 20 Cancer 70 88 Heart attack 60 Old age 80 Arrythmia 85 69 Committed Arrythmia 68 suicide 25 38 Thalassemia carrier 64 Thalassemia carrier Hysterectomy 40 40 endometriosis Old age 70 Cancer 60 Working With Human Pedigrees Predicting and Treating Genetic Disorders • Other tests analyze the fluid surrounding the fetus to detect chemical imbalances that point to specific disorders. Karyotyping Predicting and Treating Genetic Disorders • Standard tests are performed on every baby born at a hospital in the United States, whether or not the baby has any family history for a particular disease. • PKU (Phenylketonuria) Test • • a recessive disorder in which a person cannot process the amino acid phenylalanine. If the baby tests positive for phenylketonuria, the parents can put the baby on a phenylalanine-controlled diet. Such a diet is effective in preventing the mental disability that is characteristic of the untreated disorder. The test is done after 24 hours of age. A few drops of blood are taken from your baby through a heel prick. The blood test is sent to the laboratory and the result of the test will be sent to your family doctor.