* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Nature Nurture
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Fetal origins hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Pathogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of autism wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Essential gene wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Biology and sexual orientation wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
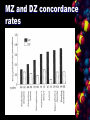
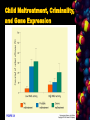
Genetics The Nature/Nurture Debate How great is the influence of genes or environment on our behavior, personality, biology, etc.? The Nature Nurture Debate Make two columns on a sheet of paper - 1) nature; 2) nurture Write characteristics you believe are mostly nature or mostly nurture in the appropriate column If the characteristic was nurture, what seemed to be the influences? The Simple View Behavior = genes + environment The Realistic View Behavior = genes + prenatal environment + parental influence + nutrition + family income + education + culture + traumas + chance … Genetics and Behavior Nucleus Cell Chromosome Gene DNA Genotype & Phenotype Genes: Essential Definitions Chromosomes – threadlike structures made of DNA that contain the genes DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) – complex molecule containing the genetic information that makes up the chromosomes – has two strands-forming a “double helix”- held together by bonds between pairs of nucleotides Genes: Essential Definitions Genes – biochemical units of heredity that make up the chromosomes – a segment of DNA capable of synthesizing a protein – The paradox 30,000 genes for 300,000 proteins Genome – the complete instructions for making an organism – consisting of all the genetic material in its chromosomes Genes: Essential Definitions Genotype -The genetic constitution of an individual. Depending on context, this may refer to the alleles at a single locus or to the complete set of genes. Phenotype -Any measurable trait of an individual. Phenotype results from an interaction between genotype and environment. Genotypic Variation Is Created by Sexual Reproduction What determines the genetic uniqueness of individuals? – Gametes – Zygote Mutations are experiments in selective advantage – Industrial melanism – Sickle-cell disease Sickle Cell Disease and Malaria - homozygotes - anemia, joint pain, swollen spleen, frequent severe infections, high rate of childhood death - heterozygotes - basically normal blood function - resistant to malaria Price for malarial resistance - homozygous sickle cell children Sexual Reproduction Combines gametes thereby creating new genotype May have evolved to outcompete parasites Genes Affect Behavior Behavioral Genetics Methods: – Twin Studies Compare MZ and DZ Twins: – Adoption Studies: Behavior Genetics Identical twins Fraternal twins Identical Twins – develop from a single zygote (fertilized egg) that splits in two, creating two genetic replicas Fraternal Twins Same sex only Same or opposite sex – develop from separate zygotes – genetically no closer than brothers and sisters, but they share the fetal environment Nature v Nurture: Twin Studies Identical (monozygotic twins) Non-identical, fraternal (dizygotic twins) Identical twins reared together same genes (relatedness of 1.0) same environment Identical twins reared apart sane genes (relatedness of 1.0) different environment Fraternal twins reared together half genes the same (relatedness 0.5) same environment Fraternal twins reared apart half genes the same (relatedness 0.5) different environment Nature v Nurture: Twin Studies Jack Yufe: raised by Jewish father in Caribbean Oskar Stoh raised by catholi grandmother i Nazi German If we had identical twins reared apart could we separate the effects of phenotype, of genotype, and of the environment. In some cases this has happened. Nature v Nurture: Twin Studies Both like sweet liqueurs Store rubber bands on their wrists Read magazines from back to front Dip buttered toast in their coffee Have very similar personalities MZ and DZ concordance rates Separated Twins Twins Studies Comparing identical twins separated at birth Twins studies movie Environmental Influences Prenatal environment Social and Environmental Contexts Influence Genetic Expression African Americans and Hypertension: a controversial theory Gene expression as concerns child maltreatment and criminality is reflected in next slide. Child Maltreatment, Criminality, and Gene Expression Temperament and genetics Suomi genetic studies on rhesus monkeys – Two alleles of one gene: the “short” version causes neurobehavioral deficits ONLY IF the infant monkey is raised with peers but without its mother The “long” version causes no neurobehavioral deficits, regardless of rearing – Maternal buffering? Behavior Genetics Adoption studies – Are adopted kids more like their biological relatives or their adopted relatives? – General findings: adoptees more like biological parents than adopted parents in intelligence and personality/temperament