* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Mendelian Genetics
Hybrid (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Pathogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genetically modified crops wikipedia , lookup
Essential gene wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
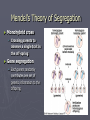
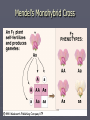
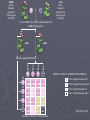
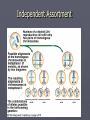
Genetics Gregor Mendel Gregor Johann Mendel ► Gregor Mendel In 1865 turned the study of heredity into a science ► His work was so brilliant and unprecedented at the time it appeared that it took thirty-four years for the rest of the scientific community to catch up to it. ► His short monograph, "Experiments with Plant Hybrids," in which Mendel described how traits were inherited, has become one of the most enduring and influential publications in the history of science. Theory of Genetic Blending ► Before Mendel’s work, plant and animal breeders based their work on the theory of “Blending”. ► This theory states that parents with different traits produced offspring of intermediate appearance. Example: Red X White flowers = Pink flowers ► When red or white flowers reappeared in future generations it was due to the instability in the genetic material Mendel’s Experimental Approach ► Mendel experimented with pea plants ► This was a great model to do genetics on Self fertilizing Cross fertilize Breed true Clear and contrasting traits Genetic terms ► Genes: segments of DNA that provide the information for traits and characteristics ► Locus: The location of a specific gene on a specific Chromosome ► Allele: alternative forms of a gene. Homologuous chromosomes Locus, the location for a specific gene A pair of alleles Three pairs of genes or Three pairs of alleles Terms cont. ► Diploid is a 2n organism with two complete sets of genetic information. ► Haploid is a 1n organism or cell with a single complete set of genetic information ► Homozygous is when both alleles for a trait are the same ► Heterozygous is when the alleles for a particular trait are different. Terms cont. ► Dominant alleles: An allele that is expressed and hides or masks “Recessive” alleles. Symbolizes as a capital letter. Example “AA” in homozygous dominant. ► Recessive allele: An allele that is expressed in the homozygous form only. Symbolized as a lower case letter Example: “aa” in homozygous recessive. Terms cont. ► Genotypes: The actual alleles that are present in an individual. Example: ► Homozygous dominant = AA ► Heterozygous = Aa ► Homozygous recessive = aa ► Phenotype: is the observable characteristic. It is the combination of genes and environment Terms cont. ►P = Parental generation ► F1 = The first generation ► F2 = The off-spring from the mating of the first generation together Mendel’s Monohybrid experiments ► Realizing that the blending theory didn’t fit with what he was observing Mendel developed an alternative hypothesis ► Hypothesis: He said “Genes are particulate factors that passes unchanged from parent to progeny unchanged”. ► Some traits mask or hide other traits Mendel’s Theory of Segregation ► Monohybrid cross Crossing parents to observe a single trait in the off-spring ► Gene segregation Each parent randomly contributes one set of genetic information to the offspring Mendel’s Monohybrid Cross Mendel’s Monohybrid Cross Probability and Punnet Squares ►A possibility of outcomes and crosses ► Test crosses Unknown genotype crossed with homozygous recessive Independent Assortment ► Do genes assort randomly in the gamets? Do some genes prefer the company of other genes? ► Example: If one is good at music are also likely to be good a math as well? AABB purpleflowered tall parent (homozygous dominant) AB aabb whiteflowered dwarf parent (homozygous recessive) ab X F1 OUTCOME: All F1 plants purple-flowered, tall (AaBb heterozygotes) AaBb AaBb meiosis, gamete formation 1/4 AB 1/4 Ab 1/4 aB 1/4 ab 1/4 AB 1/4 Ab 1/4 aB 1/4 ab ADDING UP THE F2 COMBINATIONS POSSIBLE: 1/16 1/16 1/16 1/16 9/16 or 9 purple-flowered, tall AABB AABb AaBB AaBb 1/16 1/16 1/16 1/16 AABb AAbb AaBb Aabb 1/16 1/16 1/16 3/16 or 3 purple-flowered, dwarf 3/16 or 3 white-flowered, tall 1/16 or 1 white-flowered, dwarf 1/16 AaBB AaBb aaBB aaBb 1/16 1/16 1/16 1/16 AaBb Aabb aaBb aabb Possible outcomes of cross-fertilization Fig. 11.9, p. 181 Mendel’s Theory of Segregation ► Diploid cells have pairs of genes or homologous chromosomes ► During meiosis the two genes segregate and wind up in different gametes Independent Assortment Theory in Modern Form ► Independent Assortment Gametes require genes independently of how other pairs of genes were sorted out ► Variety of Offspring Dominance Relation ► Incomplete Dominance Red snapdragon crossed with white snapdragon ---------> Pink F1 ► Codominance Multiple allele system ►ABO Blood types