* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Punnett Squares & Probability
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Pathogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Gene desert wikipedia , lookup
Gene nomenclature wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Genetically modified crops wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
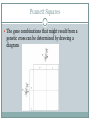
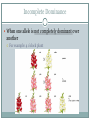
Punnett Squares & Probability WHAT IS PROBABILITY? Probability What is probability? The likelihood that a particular event will occur The principles of probability can be used to predict the outcomes of genetic crosses. Punnett Squares The gene combinations that might result from a genetic cross can be determined by drawing a diagram Tt X Tt Cross Section 11-2 Go to Section: Allele combinations Homozygous: organisms that have two identical alleles = true-breeding for a particular trait TT tt Heterozygous: organisms that have two different alleles = hybrids for a particular trait Tt Phenotype: visible, physical characteristics Tall or short Genotype: not visible, genetic makeup Homozygous or heterozygous Independent Assortment Does the gene that determines whether a seed is round or wrinkled in shape have anything to do with the gene for seed color? NO!!! The alleles for seed shape and seed color in pea plants do not influence each other’s inheritance The Principle of Independent Assortment Genes for different traits can segregate independently during the formation of gametes. Summary of Mendel’s Principles Inheritance is determined by genes passed from parents to offspring Some forms of genes are dominant and others are recessive Each offspring has two copies of a gene (alleles), one from each parent because they are segregated during gamete formation The allele for different genes usually segregate independently of one another What will happen if some alleles are neither dominant nor recessive? What will happen if some traits are controlled by more than one gene? Incomplete Dominance When one allele is not completely dominant over another For example: 4 o’clock plant Figure 11-11 Incomplete Dominance in Four O’Clock Flowers Section 11-3 Go to Section: Figure 11-11 Incomplete Dominance in Four O’Clock Flowers Section 11-3 Go to Section: Codominance Both alleles contribute to the phenotype of the organism For example: roan Multiple alleles There can be more than 2 alleles to determine phenotype. (An individual can not have more than 2 alleles for a trait, but there are more than 2 allele possible for that trait in the population) For example: blood type Polygenic traits Many traits are produced by the interaction of several genes For example: eye color skin color, height Environmental Effect Although genes are inherited, their expression can be modified by interactions with the environment. For example: sun tanning, Himalayan rabbit