* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download HT180_Presentation
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Saethre–Chotzen syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Birth defect wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Genetic testing wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Comparative genomic hybridization wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Preimplantation genetic diagnosis wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
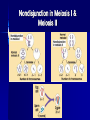
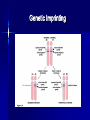
Chromosomal Abnormalities Jane Yoo HST.180 January 27, 2004 Genetic Disorders Cytogenetic Disorders Gross chromosomal abnormalities Single Gene Disorders Classical (Mendelian) inheritance Non-classical inheritance Mitochondrial genes Trinucleotide repeats Genetic imprinting Human Karyotype Idiogram of Human Karyotype Cytogenetic disorders are characterized by an abnormal constitutional karyotype What mechanisms would result in cytogenetic abnormalities? Nondisjunction in Meiosis I & Meiosis II Chromosomal Rearrangments Translocation Deletion Duplication Inversion Chromosomal Rearrangements What is the diagnosis? Trisomy 21 (Down Syndrome) The most common chromosomal disorder with an incidence of 1:700 live births in the US 95% trisomy 21; 4% Robertsonian translocation involving long arm of 21; 1% mosaic High correlation between maternal age and meiotic nondisjunction leading to trisomy 21 Congenital heart disease; dysmorphic features; mental retardation; predisposition to leukemias; neurodegenerative changes; abnormal immune response and autoimmunity Patient Interview Chromosome 2 2p25.3 myelin transcription factor 1-like 2p21 protein kinase C, epsilon 2p12-p11.1 catenin (cadherin-associated protein), alpha 2 2q14.3 caspr5 protein 2q21.2 low density lipoprotein-related protein 1B (deleted in tumors) 2q22.3 Rho GTPase activating protein 15 2q31.1-q31.2 myosin IIIB 2q33.3 amyotrophic lateral sclerosis 2 (juvenile) chromosome region, candidate 19 Single Gene Mendelian Disorders Structural Proteins --Osteogenesis imperfecta and Ehlers-Danlos (collagens); Marfan syndrome (fibrillin); Duchenne and Becker muscular dystrophies (dystrophin) Enzymes and Inhibitors --Lysosomal storage disease; SCID (adenosine deaminase); PKU (phenylalanine hydroxylase); Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency Receptors --Familial hypercholesterolemia (LDL receptor) Cell Growth Regulation --Neurofibromatosis type I (neurofibromin); Hereditary retinoblastoma (Rb) Transporters --Cystic Fibrosis (CFTR); Sickle Cell (Hb); Thalassemias (Hb) Genetic Imprinting For most (non-imprinted) genes, the maternal copy is functionally equivalent to the paternal copy Imprinted genes, however, are expressed differently from maternal and paternal alleles In most cases, imprinting selectively inactivates either the maternal or the paternal allele of a particular gene The Puzzle of Del(15)(q11q13) Mental Retardation Ataxic gait Seizures Inappropriate laughter Mental Retardation Short Stature Hypotonia Obesity Hypogonadism Genetic Imprinting Fluoresence In Situ Hybridization (FISH) Fluorescent molecules paint chromosomes to detect abnormalities Labeled probes hybridize to complementary DNA Three types of probes: locus specific, centromeric repeat, whole chromosome FISH: Many Varieties Spectral Karyotyping Comparative Genomic Hybridization (CGH) Multicolor FISH Interphase FISH Provides analysis of chromosomal aneuploidy from direct amniocyte or chorionic villus sample (CVS) preparations Screens for abnormalities in Chromosomes X, Y, 13, 18, 21 which account for 70% of chromosomal aneuploidy in the second trimester Subtelomeric probes allow for screening of terminal rearrangements Cytogenetics and FISH Interphase FISH was performed on direct CVS or amniocyte preparations from 12 reciprocal translocation and 2 Robersonian translocation pregnancies Hybridization involved 1:1 mixture of Spectrum Green labeled pter subtelomere and Spectrum Orange qter subtelomere probes Fifty interphase nuclei were scored Prenatal & Preimplantation Genetic Diagnosis (PGD) Involves creation of several in vitro embryos from the eggs and sperm of a couple Embryos develop to a 6-10 cell stage, at which point one of the embryonic cells is removed and the cellular DNA is analyzed for chromosomal abnormalities Embryos free of genetic abnormalities are subsequently transferred to women’s uterus for gestation. Embryos found carrying a genetic abnormality are discarded. Ethical & Social Implications of PGD PGD has been used in several countries for sex selection Designer baby eugenics Creating babies to save siblings from a life-threatening disease