* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Genetics
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Human leukocyte antigen wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
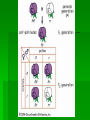
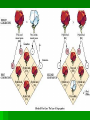
Genetics Inquiry activity: page 262 Gregor Mendel Father of modern genetics Worked with garden peas Some basic processes Fertilization – during sexual reproduction the fusion of male and female reproductive cells (two haploid cells combine to create a new diploid cell) True-breeding – pea plants that when self pollinated would create offspring identical to themselves (these where the key elements in his experiments) Genes and Dominance Mendel studied seven different traits He crossed various plants with a variety of these traits Results on page 264 Genes and dominance Genes – sections of DNA that determine certain traits (seed shape) Alleles – different forms of a gene (smooth or constricted) Some alleles are dominate (capital letter) and some are recessive (lower case) The dominate alleles mask the recessive ones Segregation Did the recessive traits dissappear? No! When Mendel crossed two of the F1 generation (first generation) the recessive alleles reappeared in the F2 generation (second generation) Segregation Mendel concluded that alleles separate from each other during the formation of gametes (sex cells) During gamete production the two alleles segregate from each other so that each gamete carries only a single copy of each gene Probability The likelihood that a particular event will occur Coin toss (independent events) Probability can be used to predict the outcome of genetic crosses Punnett Squares Shows gene combinations that might result from a genetic cross Homozygous – organisms that have two identical alleles for a trait (true breeding) Heterozygous – organisms that have two different alleles for a trait (carriers) Phenotype – physical appearance (tall) Genotype – genetic make-up