* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 8.2 Alleles and Genes Interact to Produce Phenotypes
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Human leukocyte antigen wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
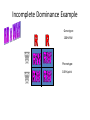
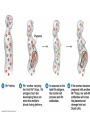
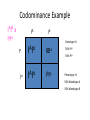
8.2 Alleles and Genes Interact to Produce Phenotypes AP Biology Radjewski Mutations • Rare inherited changes in the genetic material • Occur in genes • One allele can be mutated to a different allele Incomplete Dominance • Many genes have alleles that are neither dominant or recessive to one another. • There is an intermediate phenotype (Blend) • Example – snapdragons – RR = red – WW – white – RW = pink! • Example: Cross a red flowered Japanese 4:00 plant with a white flowered 4:00 plant Incomplete Dominance Example Genotype: 100% RW Phenotype: 100% pink Blood Types - Codominance • Codominance – Two alleles of a gene share dominance and are both expressed • In humans there is a gene I that encodes an enzyme involved in the attachment of sugars to a glycoprotein on the surface of red blood cells • There are 3 alleles of the gene: IA, IB, and IO. • The IA and IB alleles both encode active enzymes, but the enzymes attach different sugars to the glycoprotein. Blood Types Continued • The IO allele does not encode an active enzyme, so no sugar attaches • When two different alleles are present, both alleles are expressed. • The A and B glycoproteins are antigenic, which means the recipient will mount an immune response and produce antibodies against the nonself A or B cells. • The O glycoprotein does not provoke any immune responses. This makes people with IOIO good blood donors Type Antigen of Antibodies RBC in plasma A A B Can receive from O,A Can donate to A, AB B B A O.B B, AB AB A,B None O, A, B, AB AB O None A,B O O, A, B, AB Rh Factors • Rh factors are another antigen on the surface of the RBC’s • If you have this antigen/protein, you are said to be Rh+ and if you don’t have it you are Rh• Dangerous in pregnant women who are Rh- carrying a Rh+ child • During delivery, the blood mixes, so the mother will produce antibodies and the first child is unharmed • But if the second child is also Rh+, then those antibodies will attack the child’s blood cells causing severe complications – Can be treated in early pregnancy – Otherwise child will not be able to produce RBC’s and that makes oxygen levels low and death could result. Cross a person with bloodtype AB with a person with bloodtype O Codominance Example IAIB x IoIo IA IB Genotype % Io Io A o II IBIo IAIo I BI o 50% IAIo 50% IBIo Phenotype % 50% bloodtype A 50% bloodtype B Epistasis • Phenotypic expression of one trait is affected by another gene • Example in labrador retrievers – Allele B (black) is dominant over b (brown) – Allele E (pigment deposition in hair) is dominant to e (no deposition, so hair is yellow) • An EE or Ee dog with BB or Bb is black; one with ee is yellow regardless of the dominant B