* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Finally…Genetically Modified Food
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Genetically modified crops wikipedia , lookup
Genetically modified organism containment and escape wikipedia , lookup
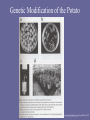
Genetically Modified Food Plan for Today •Quick foot-and-mouth disease trivia •Let’s talk about our survey results •Some background on genetically modified food A question from last time Foot-and-mouth (or hoof-and-mouth) disease • Caused by a virus that affects hoofed animals (cows, pigs, sheep, etc) – Causes blisters on the mouths and feet of infected animals, fever, lack of appetite, shivering, lack of milk production – Spreads quickly in a herd through direct contact, through the air, and via shoes/tires – Animals recover in 2-3 weeks, but are usually destroyed before then so don’t transmit disease to other animals • Rarely transmitted to humans (and only causes flu-like symptoms in humans) • No vaccine because virus mutates quickly and is cheaper to deal with outbreaks than pay for immunization Your assignment from Monday! Tally your responses to each question and write the numbers on the board: 1) 2) How effective are antibiotics at fighting colds? Have you ever taken an antibiotic at a time when you were not prescribed to do so by a doctor? 3) Do you use antibacterial soap? 4) Is it possible for a disease to become resistant to antibiotics? 5) Is it possible for a human being to become resistant to antibiotics? 6) Did you know that many farmers (particularly fruit growers) treat their crops with antibiotics? Do you know why they do that? • Are most people well-educated about antibiotics and antibacterial soap? • Are you surprised by the results? • What are some practical implications of these results? And now…genetically modified foods Which of the following does not qualify as a genetically modified food? A) B) C) D) E) Angus cattle Guernsey dairy cows Rhode Island red chickens Broccoli Corn And now…genetically modified foods F) None of the above! There are almost no foods you eat that come from naturally occurring species Farmers have been selectively breeding, crosspollinating, etc. for thousands of years Basic Genetics • Dominant & Recessive Genes • Someone might express a dominant gene but carry a recessive gene • Recessive genes from both sides can appear in subsequent generations • Plants (or animals or people) can be modified by selecting for desirable traits Plant Breeding by Trial & Error • Natural Selection – Darwin • Artificial Selection – Used for millennia for crop improvement – Select best product for future use • Artificial selection has led to much more profitable and edible crops – Higher food to waste ratio – Land produces higher yields Plant Genetic Modification (GM) • Introduce gene or genes artificially • Plants can be described as “transgenic” • Began in late 1970s – development of DNA manipulation • Gained knowledge of how to cut DNA molecules at particular points and glue back together – recombinant DNA technology • How it works: Propagate selected DNA through bacteria propagation – Cut & splice plant genes and then propagate in bacteria Genetic Modification of the Potato Genetically Modified Crops, Nigel Halford, 2003 Advantages of GM • Precision – involve only individual genes that are desirable • Genes can act on only a specific part of plant or a particular portion of its life cycle • Safety of protein produced by gene can be studied prior to use in GM program • Improved crop yields • Improved crop characteristics • Reduce pesticide use – insect resistant and/or herbicide resistant crops Disadvantages of GM • Invest more time & money than program of random mutations • Barriers and restrictions to GM crop development – regulations in some countries • Safety???? Potential Safety Concerns 1. Pleiotropy: genes have multiple functions, especially when they work in conjunction with other genes We may transfer genes that have other functions we don’t want The genes may develop new functions when they interact with a new genome Potential Safety Concerns 2. Plasmids: functions (especially undesirable ones) may transfer to other organisms in the environment 3. Pollination: When plants spread seeds, other farms could pick up transgenic traits without realizing it Potential Safety Concerns Since transgenic foods haven’t been around long, nobody can study the long-term effects of eating these foods yet And these are just the safety issues–there’s a lot more to consider! Golden Rice The vitamin A-producing gene is taken out of a red pepper and put into rice Advantage: Could save millions of children world-wide from blindness Siberian Tomatoes (Strawberries, too) The anti-freeze-producing gene is taken out of a flounder and put into tomatoes Advantage: Tomatoes that can be shipped at lower temperatures, less rotting, less waste, and more profit for tomato growers B.t. Corn An insecticidal protein from the bacteria Bacillus thuringiensis is put into corn Advantage: Corn is protected from pests, so chemical pesticides are not necessary In development: Banana Vaccine Viral proteins for infectious diseases such as Hepatitis B will be put into bananas Advantage: Ability to efficiently vaccinate people world-wide GM Statistics • In 2001, 6% of total world agriculture was GM crops • > 50% of world’s soybean crop is genetically modified • Countries growing GM crops: US, Canada, Argentina, Uruguay, Mexico, Spain, Bulgaria, Ukraine, Romania, China, South Africa, Australia Questions for you • Are the benefits of golden rice, siberian tomatoes, B.t. corn, and the banana vaccine worth the risks? Why or why not? • How do you decide what type of genetically modified food is worth the risk of eating? • The EU currently bans the importation of live genetically modified plants but does import genetically modified foods. Is this good policy?