* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slide 1
Pathogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Gene desert wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Genetically modified crops wikipedia , lookup
Gene nomenclature wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
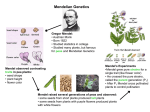
Gregor Mendel “The Father of Genetics” Sections 6.3, 6.4, 6.5 Language of Genetics • Trait Define the following 16 words • Gene • Allele • genome • Hybrid • Genotype • purebred • Phenotype • Test cross • Homozygous • Heterozygous • Dominant • Recessive • F1 generation • F2 generation • P generation Gregor Mendel Born in 1822 in Austria High School teacher at a monastery Avid gardener, studied pea plants Looked at different traits by cross-pollinating the pea flowers. The traits Mendel studied in garden pea plants The results of these studies lead to the Three Basic Principles of Genetics 1. Principle of Dominance One gene in a trait can prevent the other gene from being expressed. Gene expressed is dominant B Gene not expressed is recessive b Dominant genes Remember A trait is the same as an allele which generally is the same as a gene Today we call the inherited traits genes! 2. Principle of Segregation The two genes for each trait separate when the gametes are formed. Each gamete only carries one gene for each trait 3. Principle of Independent Assortment Genes for different traits can segregate independently during the formation of gametes Traits and Probability Law of Probability The probability of an event occurring is not influenced by the outcome of earlier events There is always a 50% chance of having a boy and a 50% chance of having a girl Product Rule The probability of two or more independent events occurring together is the product (x) of the individual probabilities of each occurring alone. Probability of a coin being tails is .5, for two coins to both be tails is .5 x .5 or .25 Now let us see how that applies to predicting outcomes in Genetic crosses The Punnett Square The parents (P generation) Have children (F1 generation) The children (F1 generation) cross with each other and have children (F2 generation) Monohybrid Cross Genotypic ratio: Phenotypic Ratio: 1 BB:2 Bb:1 bb 3 purple:1 white Dihybrid Cross A- yellow seed a- green seed B- round seed b- wrinkled seed Phenotypic ratio: 9:3:3:1 9 yellow round seeds: 3 yellow wrinkled seeds: 3 green round seeds: 1 green wrinkled seed