* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
Agarose gel electrophoresis wikipedia , lookup
Promoter (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
RNA polymerase II holoenzyme wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Eukaryotic transcription wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Restriction enzyme wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
Molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Transcriptional regulation wikipedia , lookup
Community fingerprinting wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Real-time polymerase chain reaction wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
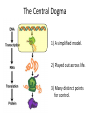
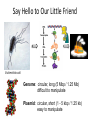
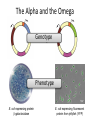
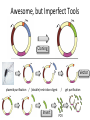
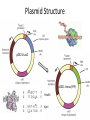
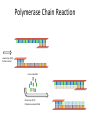
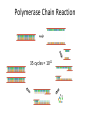
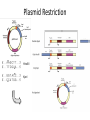
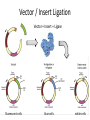
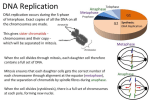
Basic DNA Science BE Bootcamp 2008 Phillips Group / Caltech Three Molecules of Life DNA: four nucleotide bases (GC,AT) (2 bits) genetic code in 3 base ‘codons’ information storage and propagation, genetic regulation Protein: folded polypeptide of 20 amino acids motility, metabolism, reproduction, genetic regulation, transport, etc. Lipid: polar / non-polar molecules separate ‘self’ from ‘non-self’ regulate material flow, cell shape, compartmentalizes, etc Three Molecules of Life DNA: four nucleotide bases (GC,AT) (2 bits) genetic code in 3 base ‘codons’ information storage and propagation, genetic regulation Protein: folded polypeptide of 20 amino acids motility, metabolism, reproduction, genetic regulation, transport, etc. Manipulating DNA – Protein Relationships: Revolutionized biological research (e.g. crystallography, fluorescent proteins as markers) and medicine (e.g. drug manufacture) The Central Dogma 1) A simplified model. 2) Played out across life. 3) Many distinct points for control. Say Hello to Our Little Friend Escherichia coli Genome: circular, long (5 Mbp / 1.25 Mb) difficult to manipulate Plasmid: circular, short (1 - 5 kbp / 1.25 kb) easy to manipulate Say Hello to Our Little Friend Escherichia coli 1) 2) 3) 4) How do we get the gene of interest onto the plasmid? How do we get the plasmid into the bacterium? How do we convince the bacterium to use this DNA? How do we tell if genes are transcribed? The Alpha and the Omega Genotype Phenotype E. coli expressing protein -galactosidase E. coli expressing fluorescent protein from jellyfish (YFP) Awesome, but Imperfect Tools Cloning Vector plasmid purification / (double) restriction digest Insert / PCR gel purification Awesome, but Imperfect Tools Cloning Vector plasmid purification / (double) restriction digest / gel purification Vector + Insert Insert PCR Ligation Transform (Electroporation) Plasmid Structure Direction of transcription Direction of transcription pZE21-Venus(YFP) Promoter – RNA polymerase binding site, transcriptional regulator Origin of Replication – site where plasmid replication begins for division, controls copy number and hence regulates Restriction Sites – sequence-specific enzymatic DNA cleavage sites, leaves sticky ends for proper insert ligation Kanamycin – encodes gene for Kanamycin (fungal) antibiotic resistance, imparts severe selective advantage in proper media Non-descript DNA – contain other restriction sites for gene insertion Plasmid Structure pZE21-LacZ pZE21-Venus(YFP) HindIII KpnI Polymerase Chain Reaction High temp (98C) DNA denatures Forward Primer Reverse Primer Lower temp (62C) Primers anneal Polymerase Chain Reaction Lower temp (62C) Primers anneal Free nucleotides Raise temp (72C) Polymerase extends DNA Polymerase Chain Reaction 35 cycles = 1011 Plasmid Restriction HindIII KpnI Vector / Insert Ligation Vector + Insert + Ligase fluorescent cells blue cells white cells Polymerase Chain Reaction